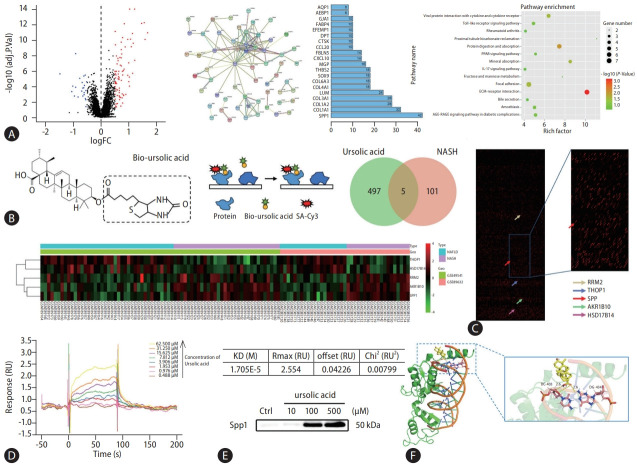
Figure 2.
Identification of SPP1 as a direct ursolic acid-binding protein. (A) Bioinformatic analysis was conducted in this study, 106 DEGs were identified from two microarrays, which notably delineated the intricate comparative stages between NAFLD and NASH, and a volcano plot was plotted. A PPI network was constructed for these DEGs using the STRING database, providing insights into the functional relationships between identified proteins. And centrality analysis, pivotal for discerning nodes of paramount importance within the network, was systematically executed based on the intricate interaction relationships between nodes. A pathway enrichment was performed to acquire a holistic understanding of the biological functions and pathways associated with the DEGs. (B) A schematic diagram showed that biotin-labeled ursolic acid was co-incubated with this array, followed by signal interpretation using Cy3-streptavidin. (C) 502 targets were identified that interacted directly with ursolic acid, and intersection analysis with the previously identified DEGs retained five candidates, wherein the differentially binding proteins were presented in the proteomics chip and heatmap. (D) The SPR analysis was produced using a biacore sensor chip, wherein the molecular dynamics analysis revealed that ursolic acid and SPP1 exhibited high-affinity interaction, with the equilibrium dissociation constant of 1.705E-5. (E) A pull-down assay was performed to further verify the binding affinity between ursolic acid and SPP1 in vivo. (F) The molecular docking simulation showed a mutual binding between ursolic acid and SPP1, with a binding energy of –5.8. SPP1, secreted phosphoprotein 1; DEGs, differentially expressed genes; NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; NASH, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis; STRING, Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes; SPR, surface plasmon resonance; KD, knockdown.