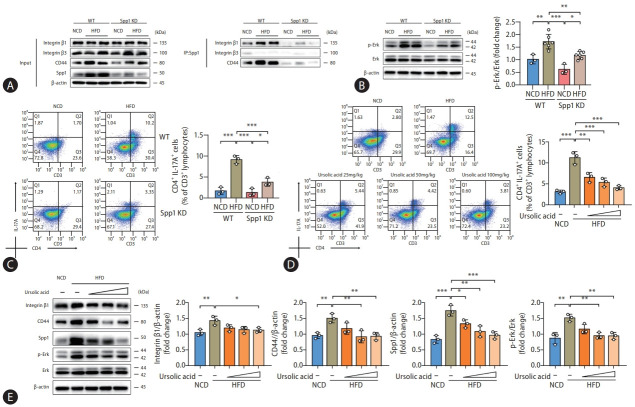
Figure 5.
Ursolic acid modulates SPP1-mediated Th17 cell differentiation to ameliorate MASLD. (A–C) Mice were derived from the experiments of SPP1 KD, wherein (A) presented that the protein levels of ITGB1 and CD44 expressed in the pull-down products were conspicuously surged by HFD administration, whereas a precipitous decline in their expression was observed in the liver tissue lysates procured from the SPP1 KD mice, while (B) demonstrated that such alterations were concomitant with trends in the phosphorylation level of ERK protein; and concurrently, (C) displayed a similar trend in hepatic Th17 cell populations. (D, E) Mice were derived from the first part of experiments, those were fed with HFD and different concentrations of ursolic acid, wherein (D) suggested that ursolic acid dose-dependently ameliorated the escalated Th17 cell populations induced by the high-fat dietary regimen, and (E) revealed consistent protein levels of SPP1, ITGB1, CD44, as well as the phosphorylation level of ERK. Data are represented as mean±SD. n=3-6. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. SPP1, secreted phosphoprotein 1; MASLD, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; KD, knockdown; ITGB1, integrin β1; CD44A, CD44 antagonists; HFD, highfat diets; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; SD, standard deviation.