FIGURE 1.
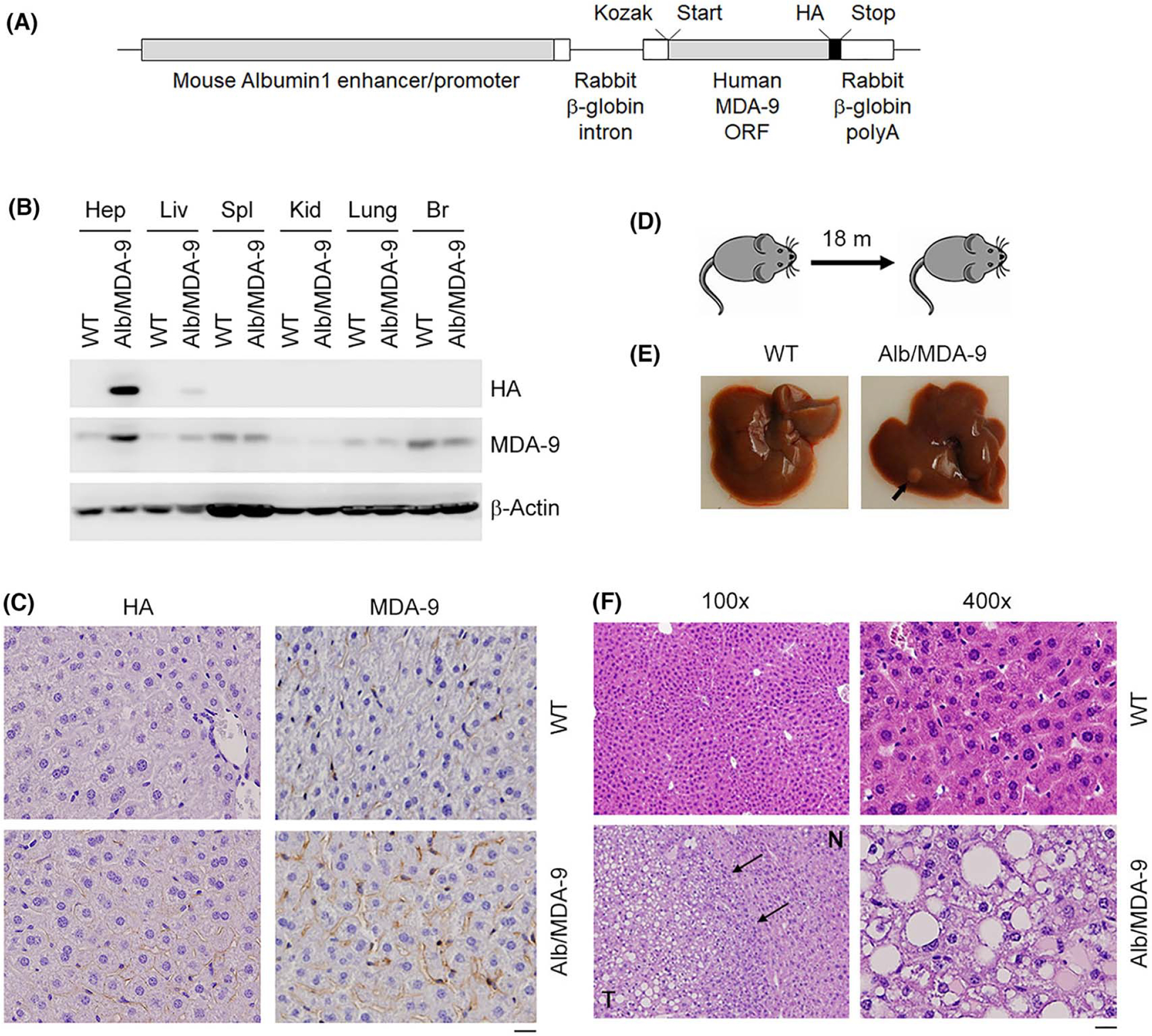
Generation and initial characterization of Alb/MDA-9 mouse. (A) The Alb/MDA-9 transgene contains a mouse Albumin1 enhancer/promoter, a rabbit β-globin intron to enhance expression, the human MDA-9 open reading frame (ORF), a C-terminal hemagglutinin (HA) tag, and a rabbit β-globin polyadenylation (polyA) region. The Kozak consensus sequence and translational start and stop codons are indicated. (B) Human MDA-9 was detected by western blot in mouse hepatocytes (Hep) and mouse tissues (liver [Liv], spleen [Spl], kidney [Kid], brain [Br]) using anti-HA and anti–MDA-9 antibodies. β-Actin was used as loading control. (C) Immunohistochemical analysis of WT and Alb/MDA-9 liver sections using anti-HA and anti–MDA-9 antibodies. Magnification: 400×. Scale bar: 20 μm. (D) Schematic of experimental protocol to detect spontaneous tumorigenesis in WT and Alb/MDA-9 mice. (E) Representative photograph of WT and Alb/MDA-9 livers at 18 months of age. Arrow indicates solitary tumor in Alb/MDA-9 liver. (F) Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of liver sections of WT and Alb/MDA-9 livers at 18 months of age. N: normal liver; T: tumor. Arrows indicate tumor margin. Scale bar: 20 μm. Alb, albumin; MDA-9, Melanoma differentiation associated gene-9; WT, wild-type.
