FIGURE 7.
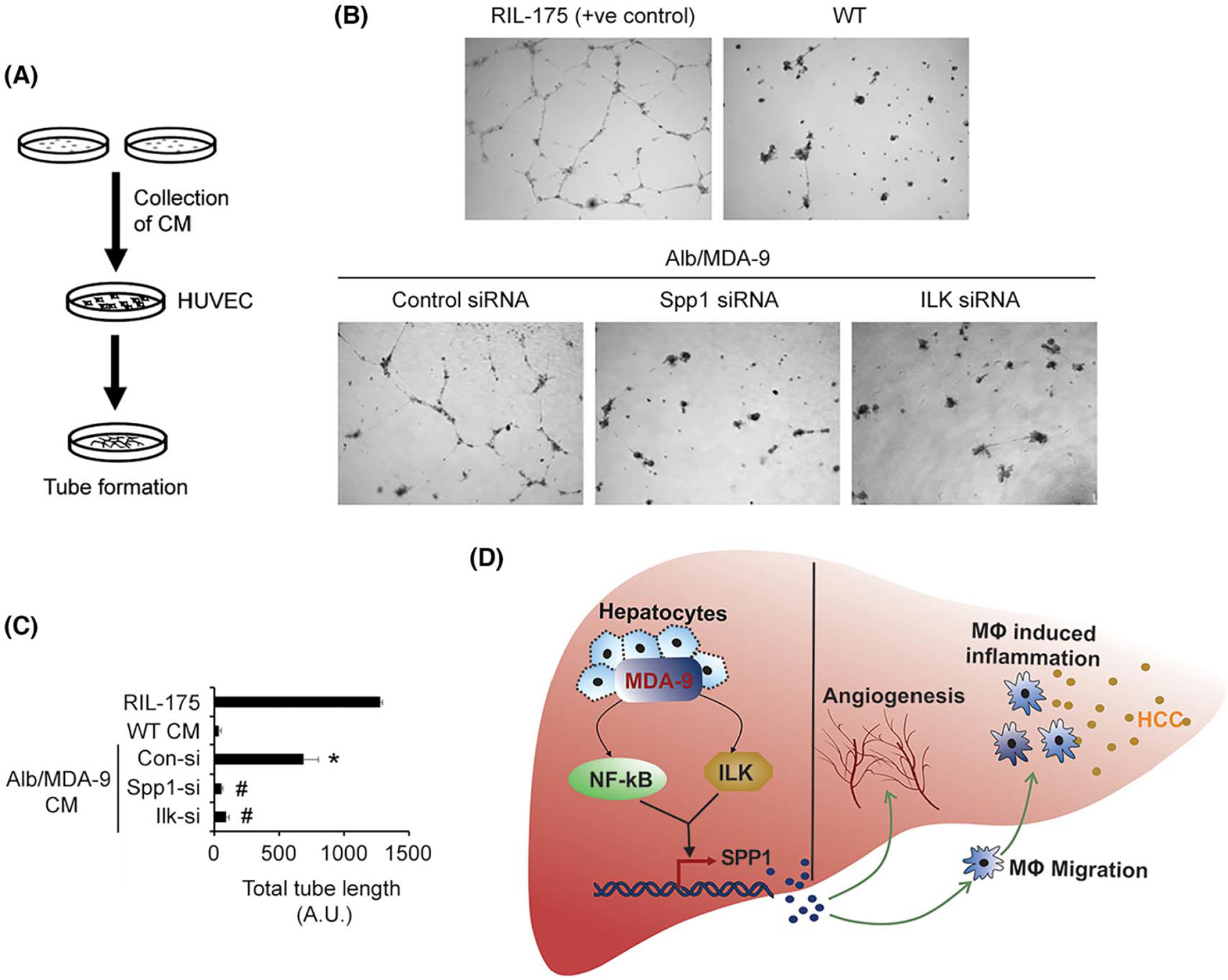
Spp1 mediates MDA-9–induced angiogenesis. (A) Schematic representation of the experimental protocol. (B) Representative photomicrographs of tube formation assay in the indicated treatment conditions. (C) Quantification of tube formation assay in the indicated treatment conditions. Data represent mean ± SEM. *p < 0.01 between WT CM and Alb/MDA-9 CM treated with control siRNA; #p < 0.01 between Alb/MDA-9 CM, treated with control siRNA, and Alb/MDA-9 CM treated with Spp1 or Ilk siRNA. (D) Cartoon showing mechanism by which MDA-9 promotes HCC. MDA-9 overexpression activates NF-κB and ILK signaling pathways, which leads to induction of Spp1 predominantly via the NF-κB pathway (thick arrow). Spp1 stimulates angiogenesis and macrophage recruitment and hence inflammation, leading to promotion of HCC. Alb, albumin; CM, conditioned medium; Con-si, control siRNA; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; HUVEC, human umbilical vein endothelial cells; ILK, integrin-linked kinase; Ilk-si, Ilk siRNA; MDA-9, Melanoma differentiation associated gene-9; siRNA, small interfering RNA; Spp1, Secreted phosphoprotein 1; WT, wild-type.
