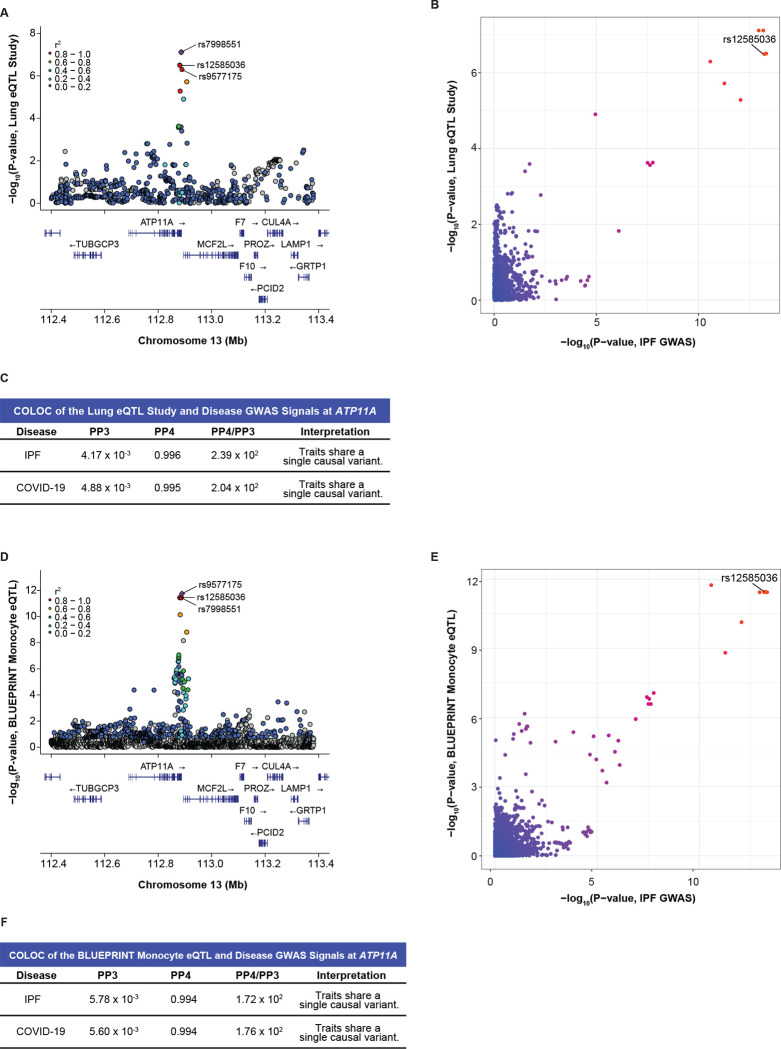
Figure 4: Colocalization at rs12585036 in a proinflammatory context and cell-type specific manner reveals ATP11A as a causal gene.
(A) LocusZoom plot shows that rs12585036 is a top eQTL and in strong LD with the lead eQTL (rs7998551; purple diamond) for ATP11A in the Lung eQTL Study, which included primarily individuals with a smoking history.
(B) Comparison of −log10(p-values) from the IPF GWAS and ATP11A-eQTLs in the Lung eQTL Study shows rs12585036 as a top shared SNP.
(C) COLOC indicates strong colocalization between the disease GWAS and the Lung eQTL Study’s ATP11A-eQTL signals with PP4 > 0.900, and PP4/PP3 > 5.00.
(D) rs12585036 is a top eQTL and in strong LD with the lead eQTL (rs9577175) for ATP11A in monocytes in the BLUEPRINT project.
(E) Comparison of −log10(p-values) from the IPF GWAS and monocytic ATP11A-eQTLs shows rs12585036 as a top shared SNP.
(F) COLOC indicates strong colocalization between the disease GWAS and monocytic ATP11A-eQTLs signals with PP4 > 0.900 and PP4/PP3 > 5.00.
P-values are −log10 transformed. Linkage disequilibrium information for European populations was obtained from LDlink and is relative to the lead variant in each plot.