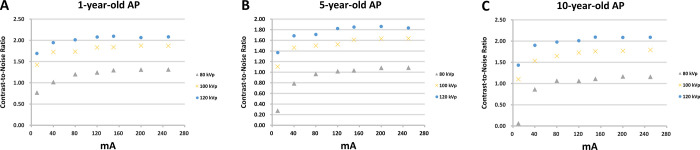
Fig 4.
The relationships between contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) and exposure voltages/currents for 1-, 5-, 10-year-old AP heads (A, B, and C, respectively). (right) Phantom induced by 80 kVp/80 mA, 80 kVp/120 mA, and 80 kVp/150 mA. The assessments of contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) were performed through the entire anatomical region of interest where inserts were clearly visible (arrows). ED = effective dose; SD = standard deviation; CNR = contrast-to-noise ratio.