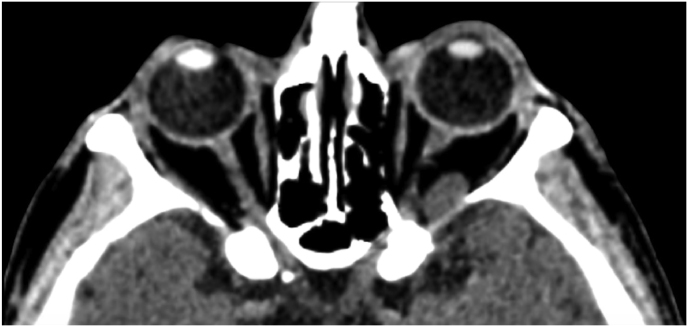
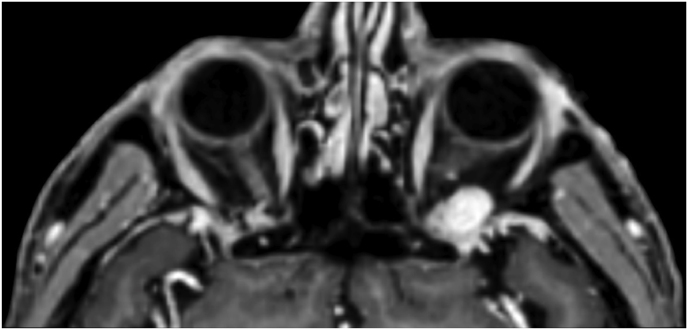
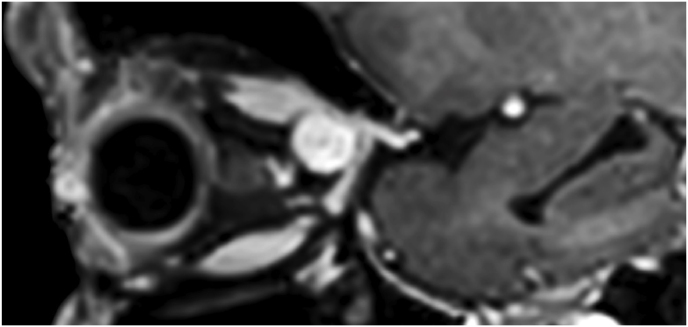
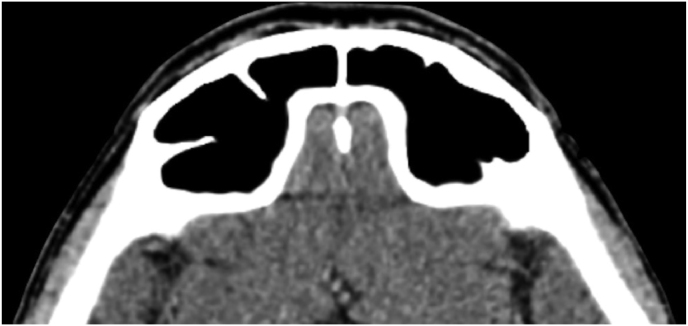
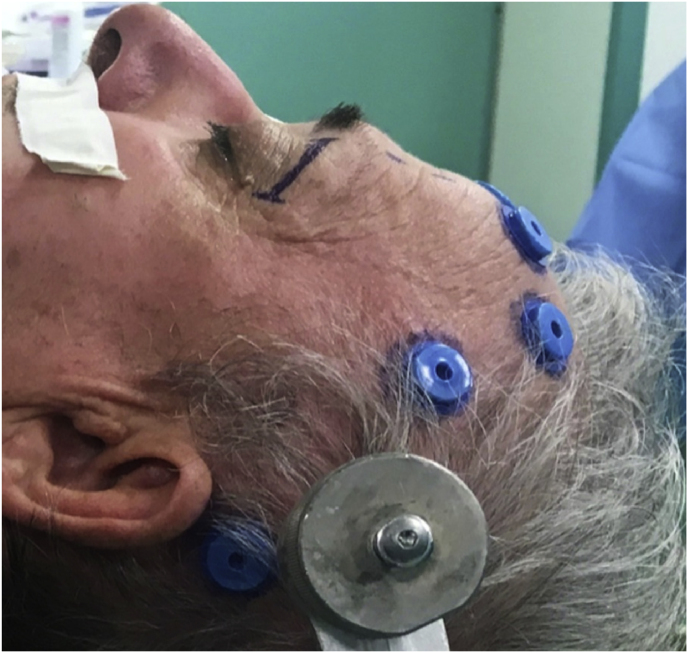
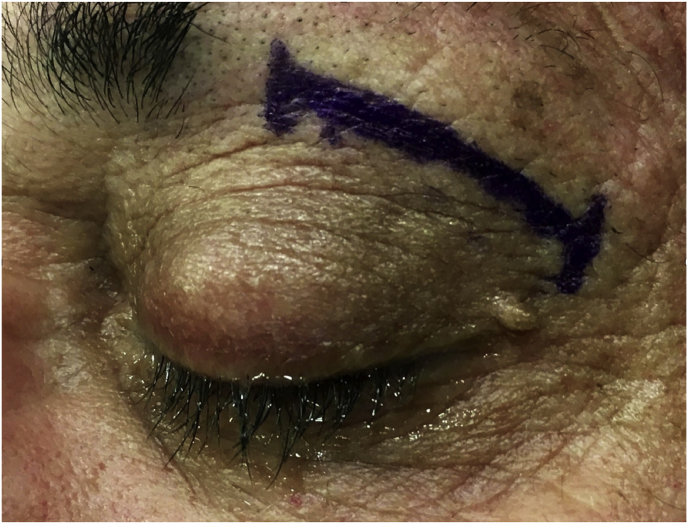
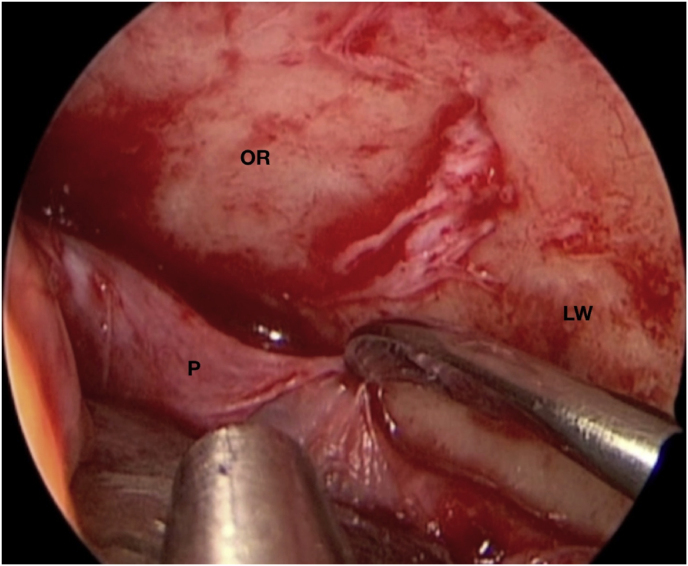
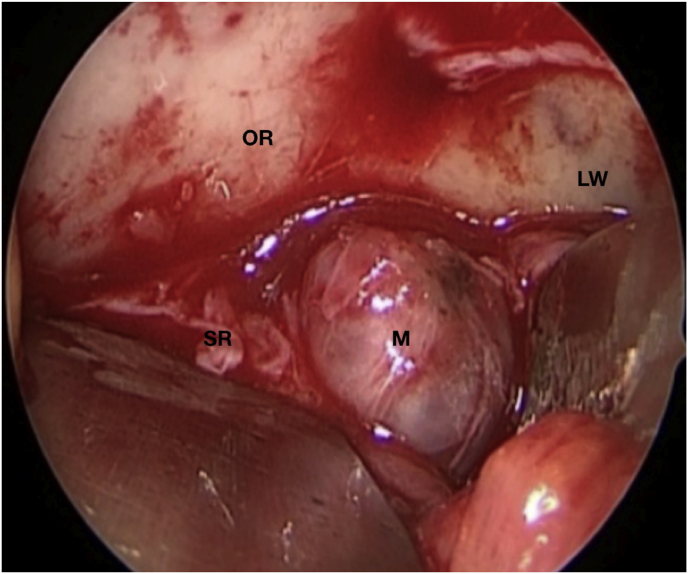
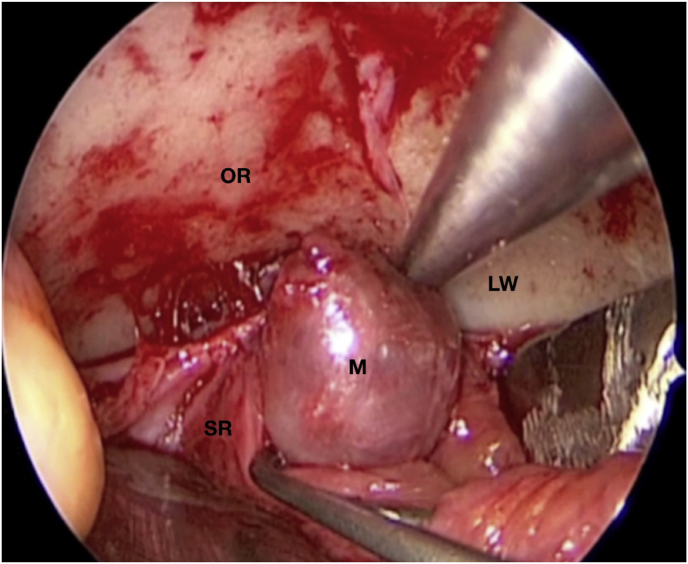
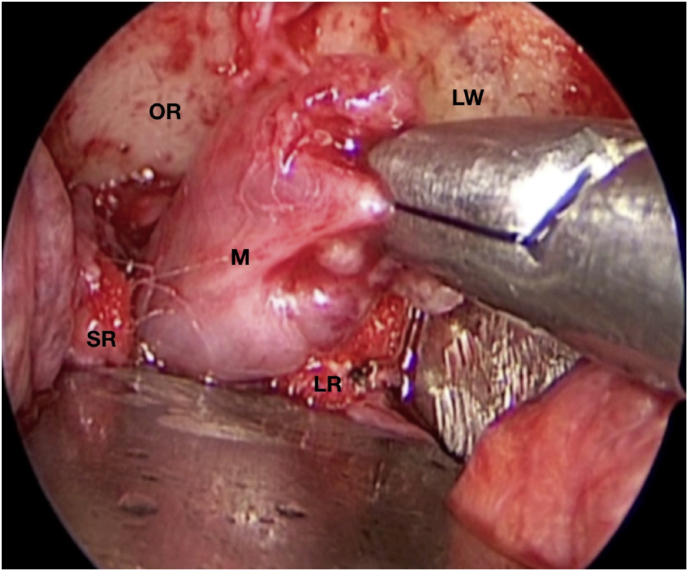
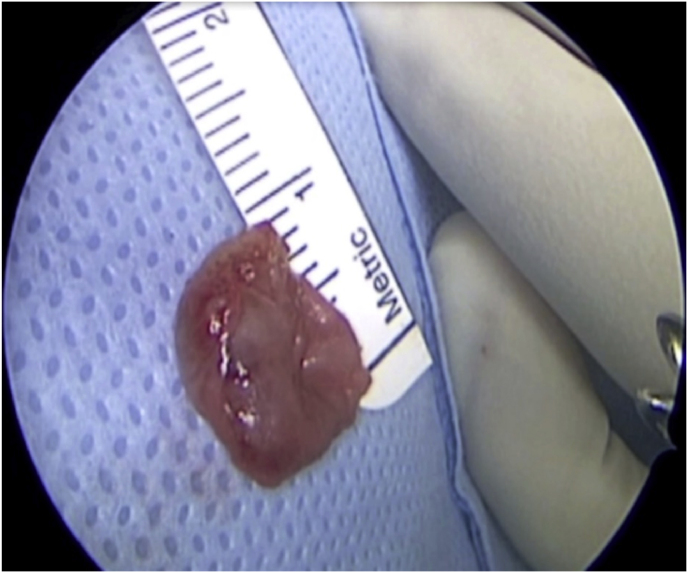
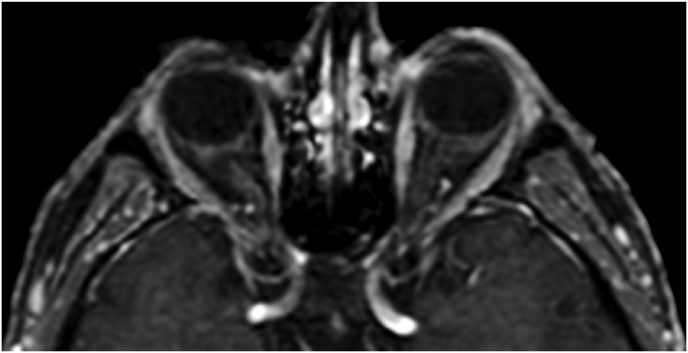
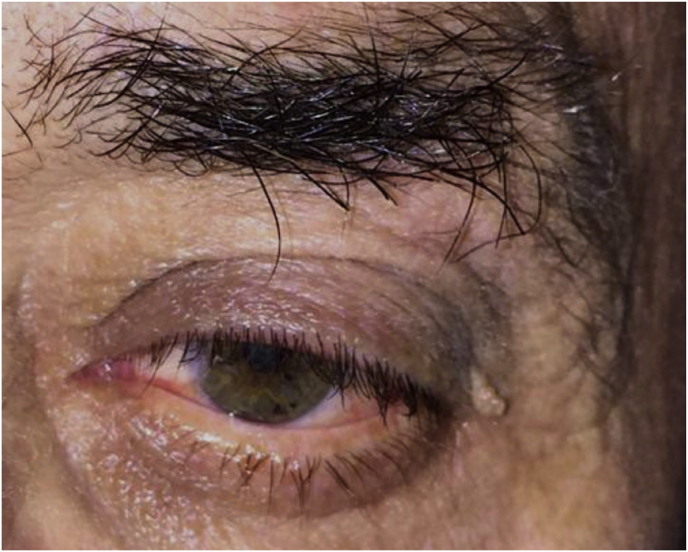
Fig. 1.
(a) Axial CT of the orbital region showing an isodense left intraconal lesion; Axial (b) and sagittal (c) T1-weighted gadolinium contrast-enhanced MRI showing a hyperintense left intraconal meningioma at the orbital apex involving the lateral compartment; (d) Axial head CT revealing hyperpneumatization of the frontal sinus; (e) Intraoperative image showing patient placed in supine position. The head was fixed with a three-point skull clamp; (f) Intraoperative photograph showing the lateral eyebrow skin incision; (g–j) The “two-surgeons and four-hands” technique allowed excision and complete removal of the tumor (Simpson grade I). OR: orbital roof; LW: lateral orbital wall; M: meningioma; P: periorbita; SR: superior rectus muscle; LR: lateral rectus muscle; (k) photograph of the operative specimen; (l) Axial T1-weighted gadolinium contrast-enhanced MRI of the orbits at 6-month follow-up revealing complete tumor removal, preserved integrity of all the intraconal structures, and no evidence of recurrence; (m) Patient photograph obtained 6 months after surgery and showing good cosmetic results in the affected eye.