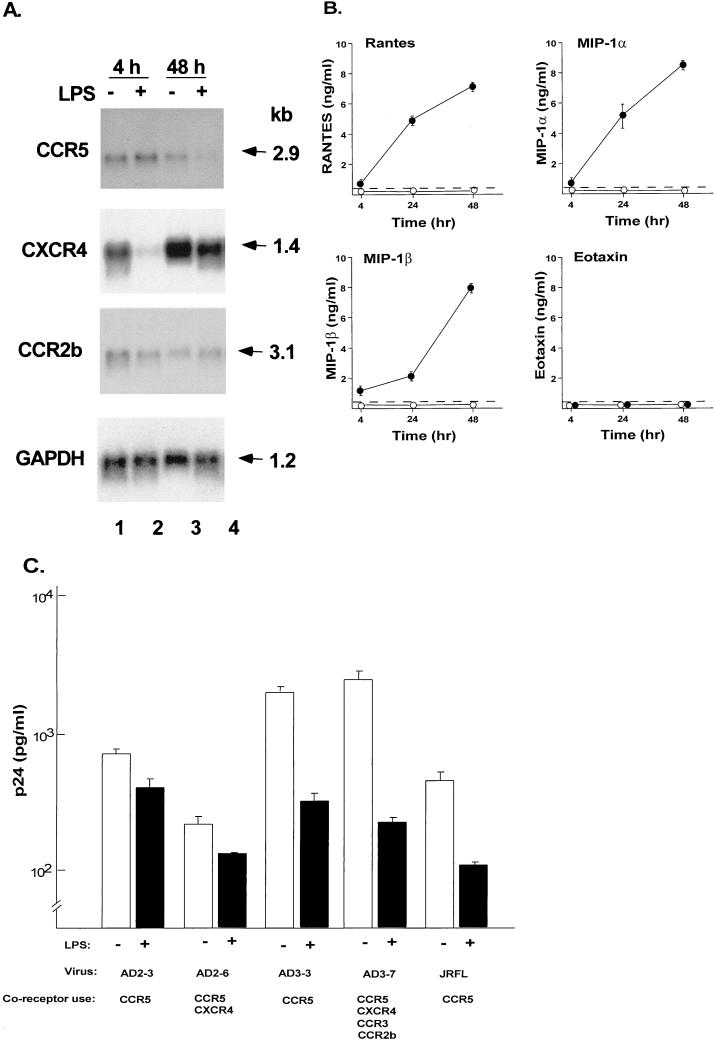
FIG. 6.
Consequences of activation of AM on HIV-1 coreceptor expression, chemokine expression, and the ability of AM to be infected by primary isolates of HIV-1. (A) AM were stimulated with LPS (100 ng/ml) for either 4 or 48 h and then analyzed for HIV-1 coreceptor expression by Northern analysis. CCR5, CXCR4, and CCR2b expression analyzed by Northern analysis in unstimulated (−) and LPS-stimulated (+) cells. GAPDH expression is used as a control. The sizes of the mRNAs are indicated in kilobases (kb). This pattern is representative of three different donors analyzed. (B) RANTES, MIP-1α, MIP-1β, and eotaxin secretion in culture supernatant as measured by ELISA following stimulation of AM with LPS (●) or without LPS stimulation (○). Dashed line represents the limit of detection of the assay. (C) Influence of LPS stimulation on HIV-1 replication in AM. AM were stimulated with LPS for 12 h and then infected with five primary HIV-1 isolates. After 14 days, HIV-1 p24 antigen levels in the supernatant were measured by ELISA. Shown are data obtained with (+) and without (−) LPS stimulation. The HIV-1 isolates are the same as in Fig. 1, and the coreceptor use of these isolates is indicated. Data are means ± standard errors of the means of triplicate measurements.