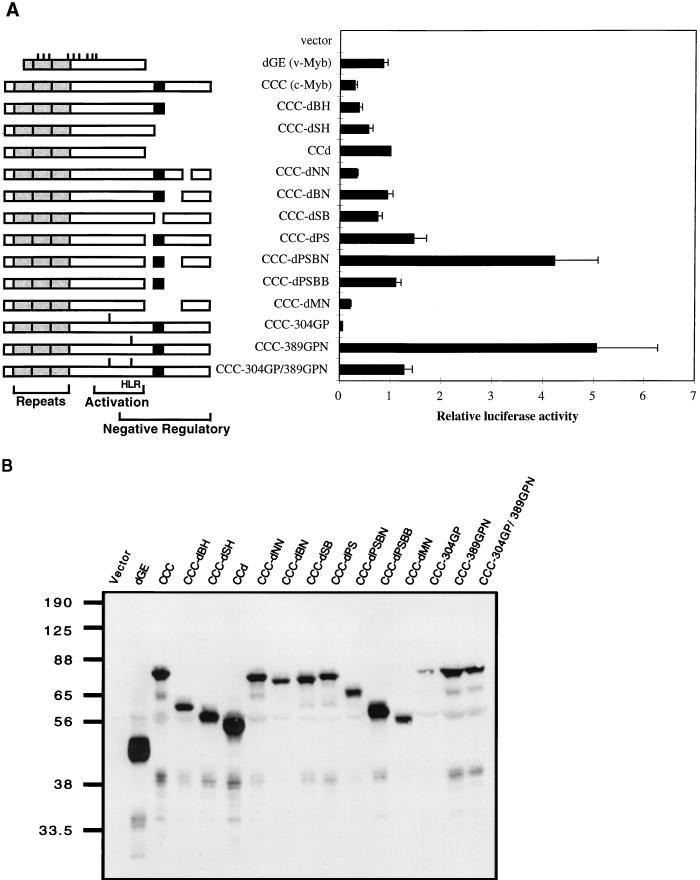
FIG. 1.
Transactivation of the EW5 reporter gene by c-Myb mutants. (A) A series of deletion or insertion mutants of c-Myb expressed from a retroviral vector were assayed for transcriptional activity in QT6 cells by transient transfection. For each transfection, 3 μg of activator and 1 μg of EW5 reporter were cotransfected into QT6 cells, along with 0.5 μg of a β-galactosidase-expressing vector (CMV-β-Gal) as an internal control. Half of the cells from each transfection were used to determine transactivation activity, as described in Materials and Methods. The other half of the cells were reserved for immunoblotting. Relative luciferase activities were obtained by assigning the luciferase activity of CCd a value of 1. Shown are the mean values of relative luciferase activities from at least three transfections and average deviations (error bars) from the mean. Schematic diagrams of c-Myb mutants are shown at the left. The point mutations in v-Myb are indicated as short bars above the v-Myb diagram. The gray boxes represent the DNA-binding domain and are also marked by repeats. The C-terminal most highly conserved domain is shown as a black box. The linker insertions are indicated as bars above the diagrams for CCC-304GP, CCC-389GPN, and CCC-304GP/389GPN. (B) Representative immunoblot of transiently transfected QT6 cells from the experiments whose results are shown in panel A. Cell lysates with equal amounts of β-Gal activity were resolved on an SDS–10% PAGE gel and immunoblotted with anti-Myb antibodies (5E and 2.7). The relative mobilities of protein markers are indicated in kilodaltons.