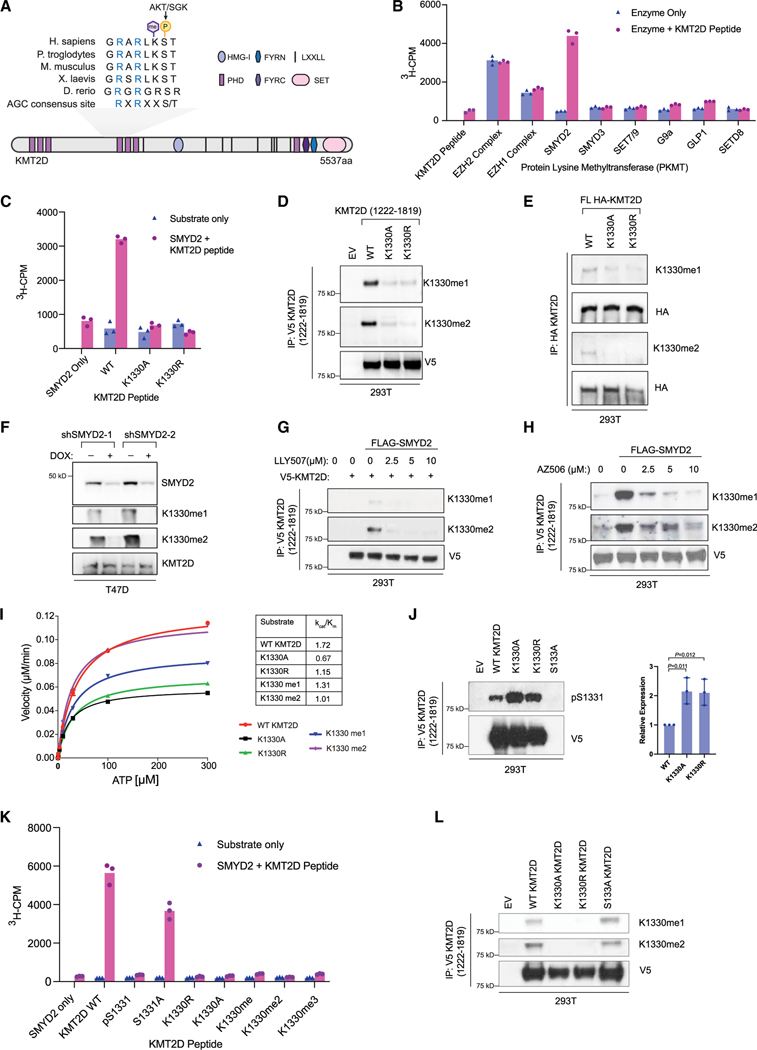
Figure 1. KMT2D is methylated by SMYD2 at K1330.
(A) Schematic showing the domain structure of lysine methyltransferase KMT2D and the conserved AGC consensus site containing both the S1331 phosphorylation site modified by AKT/SGK1 (previously published) and the identified methylation site at K1330. Sequence alignments for the indicated species were performed using Clustal W2.
(B) In vitro screen of recombinant protein lysine methyltransferases (PKMTs) to identify the methyltransferase able to catalyze K1330me. Radiometric assays were conducted using 3H-S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM) and a KMT2D peptide (amino acids [aa] 1,321–1,343) and activity was measured as 3H counts per minute (3H-CPM) using liquid scintillation counting. Peptide only and enzyme only controls were included to indicate background signal from the KMT2D peptide and PKMTs respectively (n = 3 biological replicates, representative shown).
(C) Radiometric methylation assay as in (B), using the wild-type KMT2D peptide and KMT2D peptides with the K1330 site mutated to alanine (K1330A) or arginine (K1330R).
(D) Fragment constructs of KMT2D (aa 1,222–1,819) with a c-terminal V5 tag were overexpressed in HEK293T cells and immunoprecipitated using V5-conjugated agarose beads. Wild-type KMT2D was compared to K1330A/R mutant constructs generated with site-directed mutagenesis. Site-specific antibodies (Eurogentec) were used to detect K1330me1 and K1330me2.
(E) Full-length (FL) wild-type or mutant KMT2D constructs with an N-terminal HA tag were expressed in HEK293T cells and immunoprecipitated using HA-conjugated agarose. Site-specific antibodies were used to detect K1330me1/2 modifications on full-length KMT2D.
(F) Lysates from stable T47D cell lines with two different doxycycline-inducible shRNAs were used to detect changes in K1330me1/2 upon loss of SMYD2.
(G) Wild-type V5-tagged KMT2D constructs were co-expressed with wild-type SMYD2 in HEK293T cells and treated with the indicated doses of LLY507, a catalytic inhibitor of SMYD2, for 48 h before collection. Following immunoprecipitation, samples were subjected to immunoblot with K1330me1/2 antibodies.
(H) Same as in (G) but with a different catalytic inhibitor of SMYD2, AZ506.
(I) Kinetic analysis of recombinant AKT1 activity on KMT2D wild-type, mutant, or modified peptides. Reactions were conducted using 33P-ATP and detected using a radiometric filter-binding assay (Reaction Biology).
(J) V5-tagged fragment wild-type KMT2D and point mutants were overexpressed and immunoprecipitated from HEK293T cells, followed by immunoblot with the pS1331 antibody. One representative western blot is shown and the differences in pS1331 are quantified on the right (n = 3 biological replicates, mean, SD). Indicated p values were calculated using an unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t test.
(K) In vitro methylation assay using recombinant SMYD2 and wild-type, mutant, or modified KMT2D peptides (aa 1,321–1,343), conducted as in Figures 1B and 1C.
(L) V5-tagged fragment wild-type KMT2D and point mutants were overexpressed and immunoprecipitated from HEK293T cells, followed by immunoblot with K1330me1/me2 antibodies.