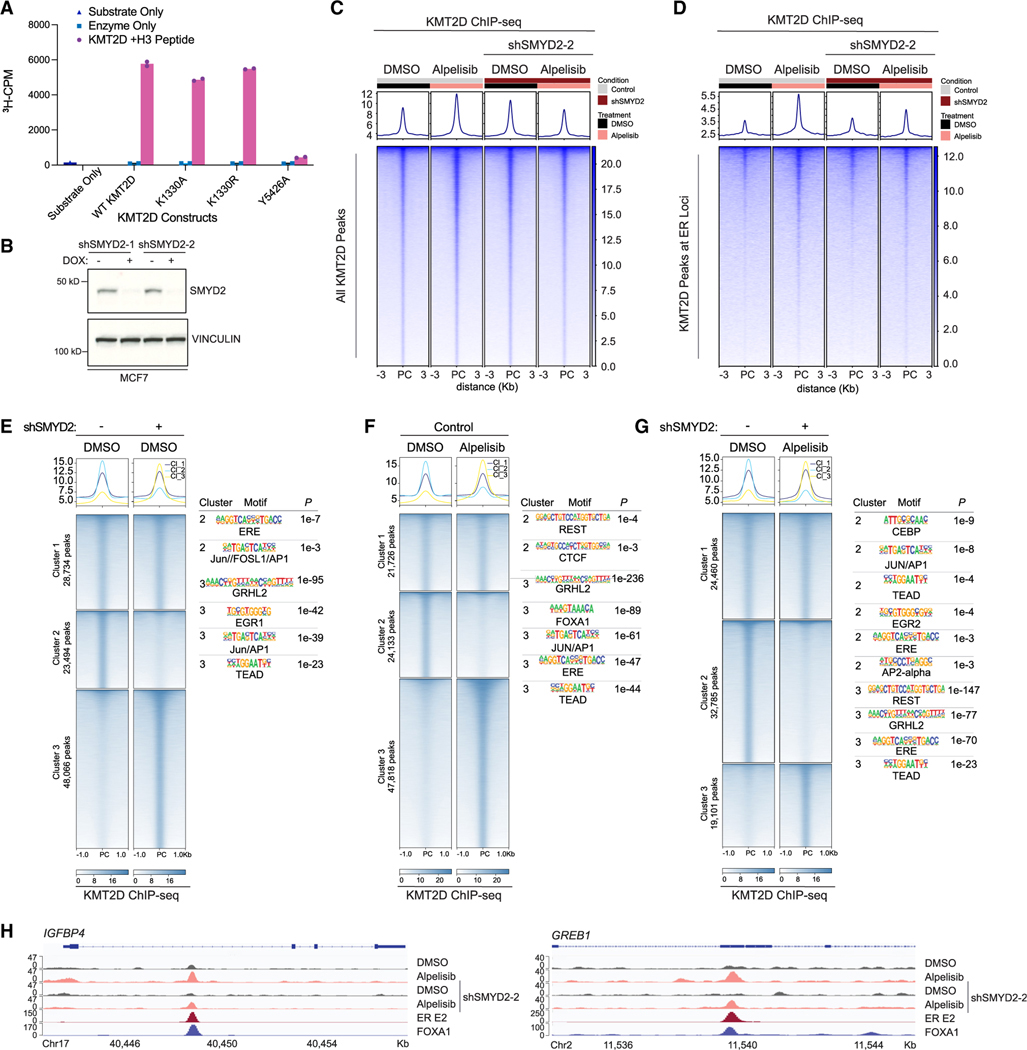
Figure 2. SMYD2 methylation of KMT2D affects KMT2D binding genome-wide and cofactor associations in breast cancer.
(A) In vitro methylation assay to assess activity of immunoprecipitated full-length KMT2D wild type and mutants on an H3 peptide substrate (aa 1–21). A catalytic-dead mutant of KMT2D (Y5426A) was used as a control. Substrate only and enzyme only samples were used to control for background signal from the H3 peptide and KMT2D mutants respectively (n = 3 biological replicates, representative shown).
(B) Western blot of SMYD2 and vinculin in MCF7 cells transduced with shSMYD2–1 or shSMYD2–2.
(C) Tornado plot of KMT2D ChIP-seq showing global binding sites of KMT2D in MCF7 cells with doxycycline-inducible SMYD2 knockdown. Cells were treated with DMSO or 1 μM PI3Kα inhibitor alpelisib for 8 h before crosslinking.
(D) KMT2D binding at estrogen receptor (ER) target loci (GEO: GSE59530) in all aforementioned conditions.
(E–G) Cluster analysis of KMT2D ChIP-seq peaks comparing SMYD2 knockdown alone (E), alpelisib treatment alone (F), and the combination of SMYD2 knockdown and alpelisib treatment (G). HOMER motif analysis for the clusters with differential KMT2D binding was performed with top significant motifs shown to the right of their respective heatmaps.
(H) KMT2D binding at ER-FOXA1 target genes IGFBP4 and GREB1 with SMYD2 knockdown and/or alpelisib treatment.