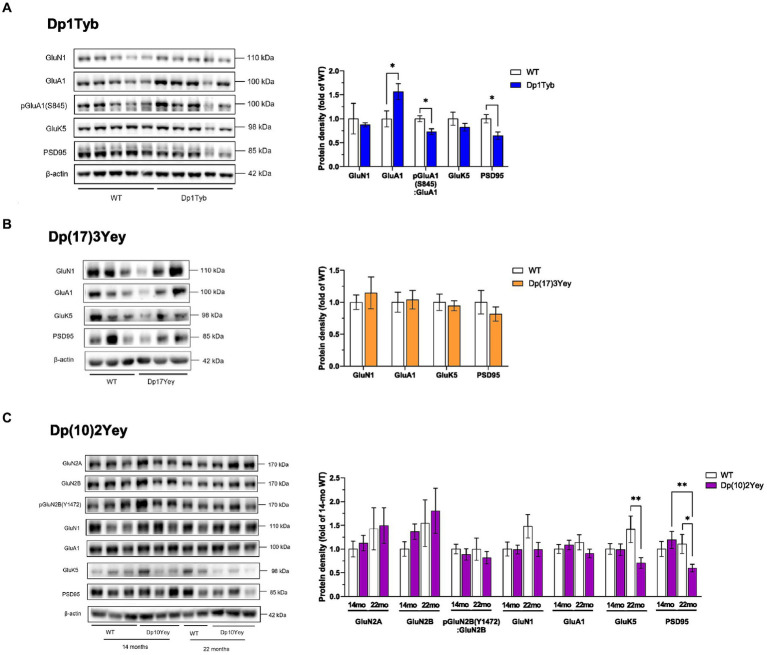
Figure 6.
Altered abundance of glutamate receptor subunits in HPC synaptosomes from Dp1Tyb, Dp(17)3Yey, and Dp(10)2Yey male mice. (A–C) HPC synaptosomes from the indicated mouse strains were analyzed by immunoblotting for glutamate receptor subunits and PSD95. Example immunoblots are shown on the left and mean ± SEM protein abundance on the right, normalized to β-actin (or to GluA1 or GluN2B in case of phosphorylation levels of the respective receptor) and then to the mean signal in WT mice. Immunoblots show analysis of HPC synaptosome extracts from 2 to 5 mice of each genotype. Compared to WT littermates, mutant Dp1Tyb mice displayed lower hippocampal expression of GluA1, pGluA1(S845), and PSD95 (Student’s t-test, *p < 0.05) (A). Mutant Dp(10)2Yey mice displayed an age-dependent decrease in hippocampal expression of GluK5 and PSD95 compared to WT littermates (two-way ANOVA, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.001) (C). The decrease in GluK5 expression was not driven by age-dependent changes in the WT group as this comparison was not statistically significant (p > 0.05) (C). 21-month-old Dp1Tyb: n = 6 WT, 5 Dp1Tyb; 21-month-old Dp(17)3Yey: n = 9 WT, 12 Dp(17)3Yey; 14-month-old Dp(10)2Yey: n = 9 WT, 11 Dp(10)2Yey; 22-month-old Dp(10)2Yey: n = 6 WT, 10 Dp(10)2Yey.