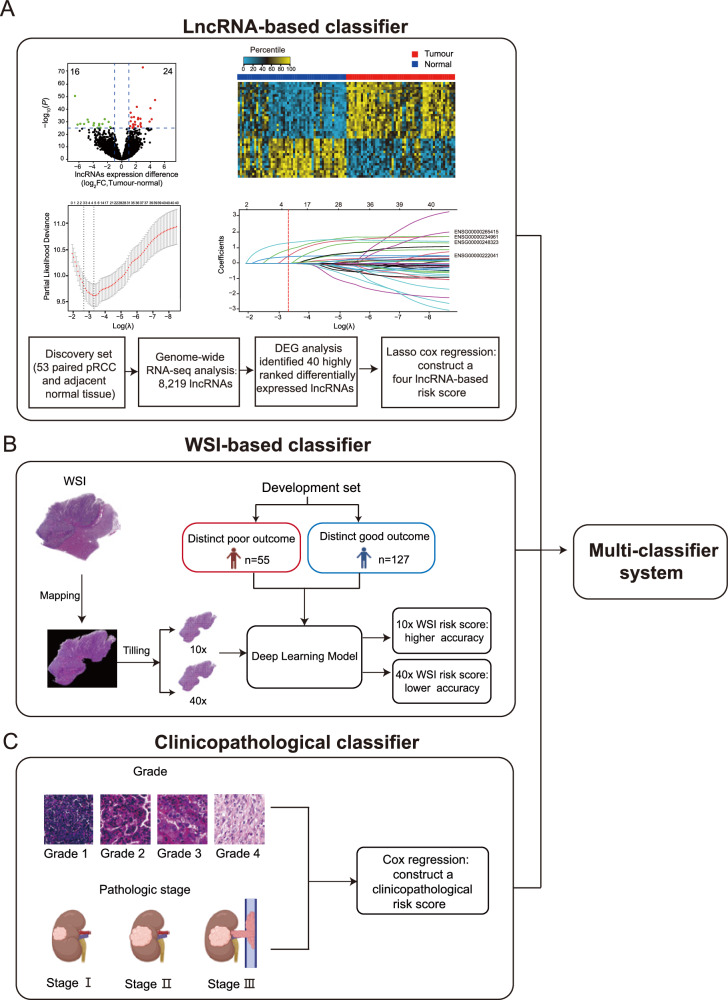
Fig. 1. Construction of the multi-classifier system.
lncRNA expression data, WSIs, and clinicopathological factors were used to develop the three classifiers respectively. We then integrated the three classifiers to develop a multi-classifier system. A The development of the lncRNA-based classifier. Upper left of panel: volcano plot comparing lncRNA expression in pRCC versus adjacent normal tissues (n = 53). Biological significance (log2 fold change (FC)) is depicted on the x axis, and the statistical significance (−log10 P) is depicted on the y axis. Forty lncRNAs were identified with a log2 FC > 1, and the false discovery rate was <10−25. Upper right of panel: heat map showing the expression level of 40 lncRNAs in 53 paired pRCCs. Middle left of panel: LASSO Cox regression analysis to select lncRNAs to include in the classifier. The two dotted vertical lines were drawn at the optimal values using the minimum criterion (right) and 1 minus the standard error (1−s.e.) criterion (left). Middle right of panel: LASSO coefficient profiles of the 40 differentially expressed lncRNAs. A vertical line was drawn at the optimal value using the minimum criterion, which resulted in four non-zero coefficients. Four lncRNAs were finally selected using the LASSO Cox regression model to build the four lncRNA-based score. Lower panel: flow chart. B The development of the WSI-based classifier using deep learning. C The development of the clinicopathological classifier. Pictures of pathologic stages were created with BioRender.com. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.