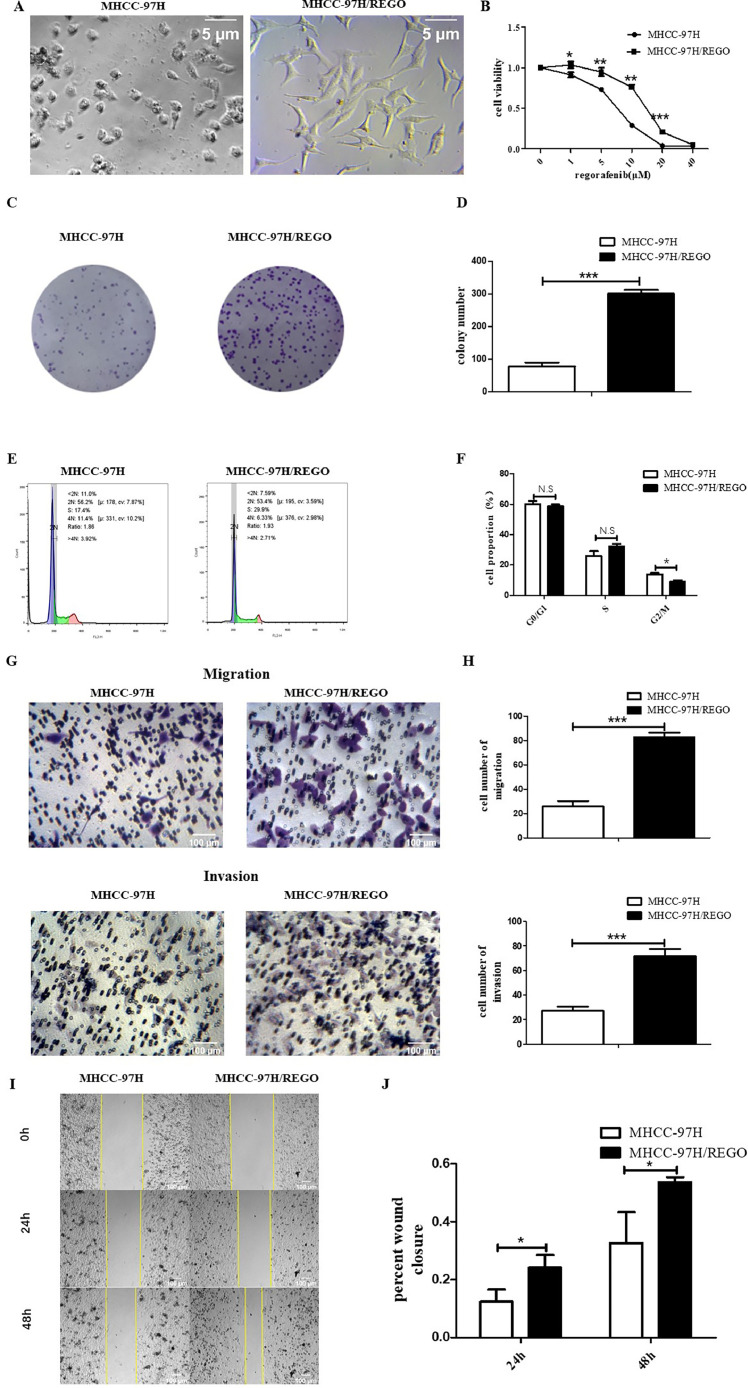
Fig. 1.
In vitro characterization of regorafenib-resistant cells.
A. MHCC-97H/REGO cells showed a fibroblast-like and mesenchymal morphology. MHCC-97H and MHCC-97H/REGO cells were photographed with a microscope at 100× magnification. B. MHCC-97H and MHCC-97H/REGO cells were treated with different concentrations of regorafenib for 72 h. Cell viability was determined by the CCK-8 assay. The IC50 values for MHCC-97H and MHCC-97H/REGO were 7.16 ± 0.46 μM and 13.78 ± 1.02 μM, respectively. C-D. Colony formation experiments with MHCC-97H and MHCC-97H/REGO cells after cell culture for 7 days. Cells were plated at a density of 103 cells per well. E-F. Flow cytometry analysis was conducted to examine the cell cycle distribution of MHCC-97H/REGO and MHCC-97H cells. G-H. The migration and invasion abilities of MHCC-97H and MHCC-97H/REGO cells were determined by Transwell experiments. In each group, 8 × 104 cells were plated, and the number of cells passing through the Transwell chamber was recorded 24 h later. I-J. Migration ability of MHCC-97H and MHCC-97H/REGO cells was determined by wound-healing migration assays. Photos were taken after 0 h, 24 h and 48 h of culture, after which the healing rate was calculated. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (one-way ANOVA).