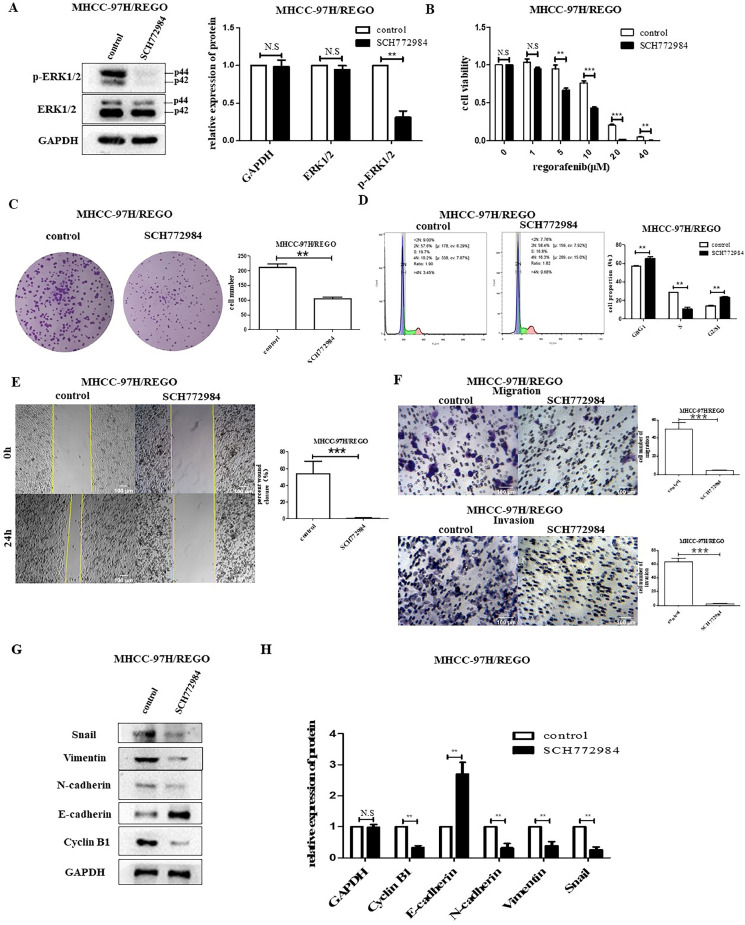
Fig. 3.
Effect of p-ERK on regorafenib resistance in the MHCC-97H/REGO cell line.
A. The expression of t-ERK and p-ERK in MHCC-97H/REGO cells treated with SCH772984. B. Cell viability was determined by the CCK-8 assay. The IC50 values for MHCC-97H/REGO- and SCH772984-treated MHCC-97H/REGO cells were 13.78 ± 1.02 μM and 7.501 ± 0.77 μM, respectively. C. Colony formation ability of MHCC-97H/REGO cells treated with or without the p-ERK inhibitor SCH772984 (5 μM). Cells were plated at a density of 103 per well and then treated with vehicle or SCH772984 for 24 h. D. Cell cycle distributions of SCH772984 treated MHCC-97H/REGO cells. E. Wound healing experiments in MHCC-97H/REGO cells treated with (right) or without (left) SCH772984 (5 µM). F. The migration and invasion ability of MHCC-97H/REGO cells were determined by Transwell experiments. A total of 8 × 104 cells were implanted into the Transwell chamber and treated with vehicle or SCH772984 (5 μM) for 24 h. G-H. Qualitative and quantitative analyses of the protein levels of E-cadherin, N-cadherin, vimentin, snail, cyclin B1, p-ERK and t-ERK in MHCC-97H/REGO cells were performed via western blotting. Cells were treated with (right) or without (left) SCH772984 (5 μM) for 24 h. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (one-way ANOVA).