Figure 3.
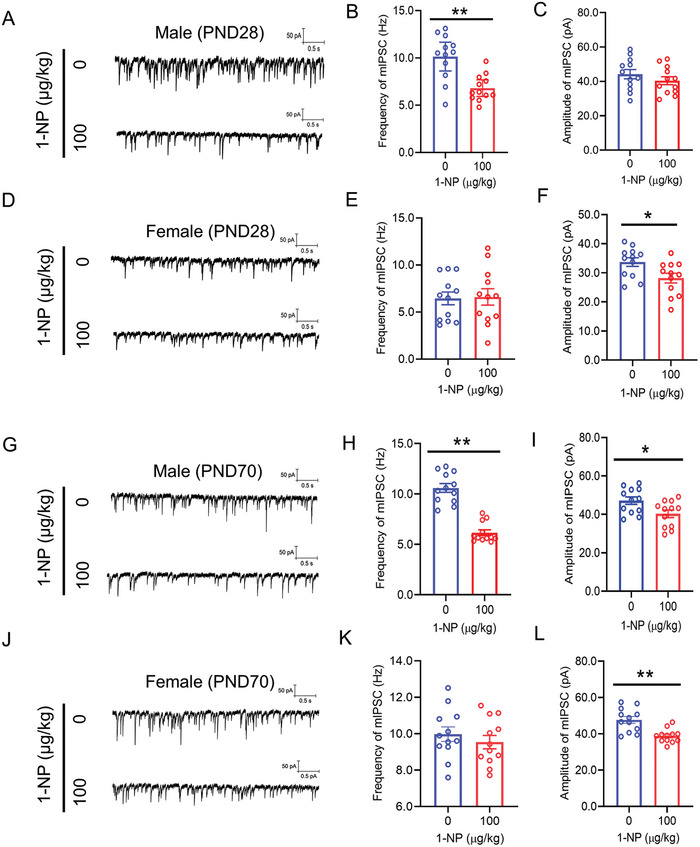
Influence of maternal 1‐NP exposure on mIPSC in offspring. 10 pregnant mice orally received different dose of 1‐NP (0, 100 µg kg−1) daily from GD0 to GD17. All pregnant mice gave birth naturally. A–F) Patch clamp was conducted on excitatory neurons to measure mIPSC in the mPFC of weaning offspring (PND28). A–C) mIPSC in the mPFC was measured in weaning male offspring. A) Representative photograph. B) Frequency of mIPSC. C) Amplitude of mIPSC. D–F) mIPSC in mPFC was measured in weaning female offspring. D) Representative photograph. E) Frequency of mIPSC. F) Amplitude of mIPSC. N = 12 excitatory neurons from 3 mice. *P < 0.05. **P < 0.01. G–L) Patch clamp was performed on excitatory neurons to measure mIPSC in the mPFC of adult offspring (PND70). G–I) mIPSC in the mPFC were measured in adult male offspring. G) Representative photograph. H) Frequency of mIPSC. I) Amplitude of mIPSC. J–L) mIPSC in the mPFC were measured in adult female offspring. J) Representative photograph. K) Frequency of mIPSC. L) Amplitude of mIPSC. N = 12 excitatory neurons from 3 mice. *P < 0.05. **P < 0.01.
