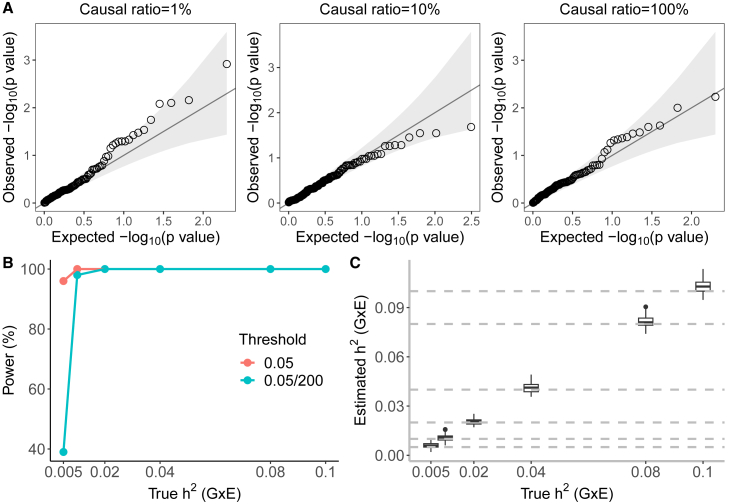
Figure 1.
Calibration and power of GENIE in simulations ( unrelated individuals, SNPs)
(A) Q-Q plot of p values (of a test of the null hypothesis of zero GxE heritability) when GENIE is applied to phenotypes simulated in the absence of GxE effects. Each panel contains 100 replicates of phenotypes simulated with additive heritability and varying proportions of causal variants. The causal ratios are the same for the G and GxE components (), and the causal SNPs for the GxE component are independently sampled to those for the additive genetic component. Across all architectures, the mean of rejection at is and for and , respectively ( is not significantly different from the nominal rate of ).
(B) The power of GENIE across genetic architectures as a function of GxE heritability. We report power for p value thresholds of .
(C) The accuracy of estimates obtained by GENIE. Across all simulations, statin usage in UKB was used as the environmental variable.