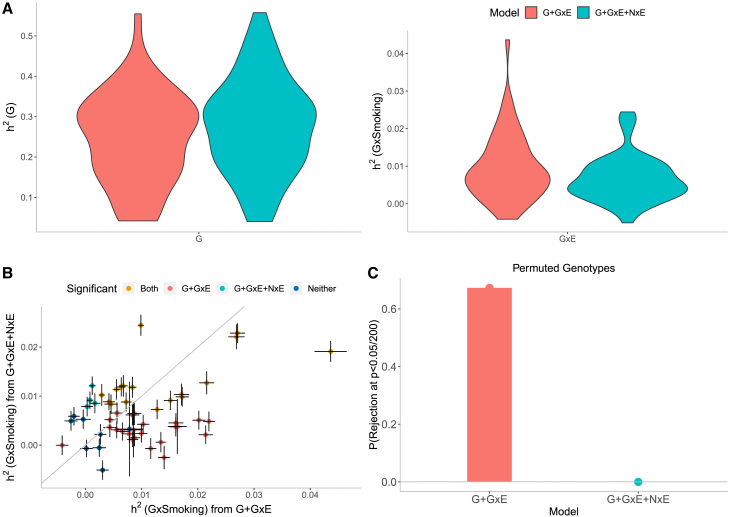
Figure 4.
Effect of noise heterogeneity (NxE) on estimates of heritability associated with GxSmoking across 50 quantitative phenotypes in UKB
Model G + GxE refers to a model with additive and gene-by-environment interaction components where the environmental variable is smoking status. Model G + GxE + NxE refers to a model with additive, gene-by-environment interaction, and noise heterogeneity (noise-by-environment interaction) components.
(A) We ran GENIE under G + GxE and G + GxE + NxE models to assess the effect of fitting an NxE component on the additive and GxE heritability estimates.
(B) Comparison of GxE heritability estimates obtained from GENIE under a G + GxE + NxE model (x axis) to a G + GxE model (y axis). Black error bars mark standard errors centered on the estimated GxE heritability. The color of the dots indicates whether estimates of GxE heritability are significant under each model.
(C) We performed permutation analyses by randomly shuffling the genotypes while preserving the trait-E relationship and applied GENIE in each setting under G + GxE and G + GxE + NxE models. We report the fraction of rejections P(p value of a test of the null hypothesis of zero GxE heritability that accounts for the number of phenotypes tested) over 50 UKB phenotypes.