Fig. 2. Telomerase generates interstitial and terminal telomeric repeat arrays.
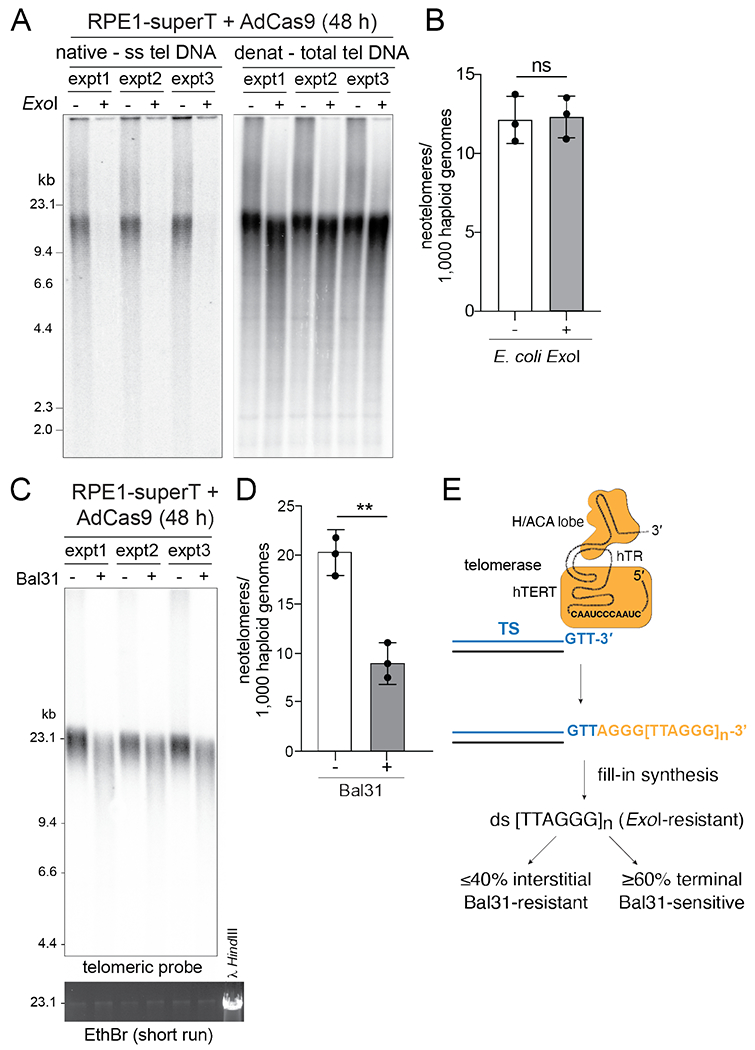
(A) Telomeric overhang assay to monitor the effect of E. coli ExoI treatment. DNAs from RPE1-superT cells at 48 h after infection with AdCas9 with or without ExoI treatment were digested with MboI/AluI and analyzed by in-gel hybridization to a telomeric C-strand probe (left). The gel denatured, and the total telomeric DNA was detected by rehybridization with the same probe (right). (B) Quantification of neotelomeres by TaqMan qPCR on the DNA samples shown in (A). (C) Southern blot for telomeric DNA showing the expected shortening effect of telomeric restriction fragments by Bal31 treatment of intact genomic DNA. DNAs were from three independent AdCas9 infections of RPE1-superT cells. EthBr staining of large-MW DNA fragments shows that Bal31 has not degraded bulk genomic DNA. (D) Quantification of neotelomeres by TaqMan qPCR on the DNA samples in (C). (E) Summary of the fate of the TTAGGG repeats added by telomerase. Mean ± SD of 3 biological replicates. ns, not significant; p > 0.05, ** p < 0.01, based on two-tailed ratio-paired t-test in (A), (D), and (F).
