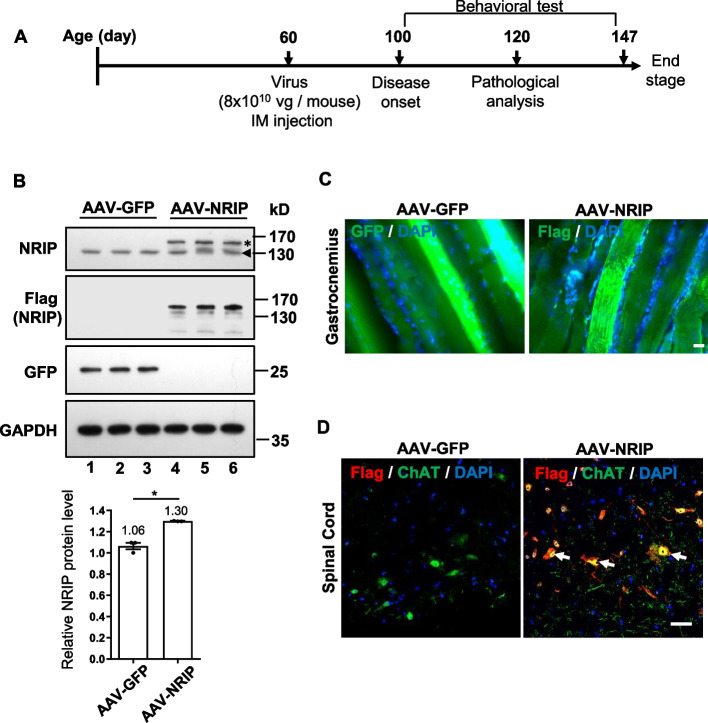
Fig. 2.
The gene therapy of SOD1 G93A via intramuscular injection of AAV-NRIP (A) Schematic representation of AAV-NRIP gene therapy. AAV-NRIP and AAV-GFP were delivered into the gastrocnemius (GAS) muscles of SOD1 G93A mice at postnatal day 60 through intramuscular injection. Behavioral tests were conducted from the age of 100 days (post-infection day 40) to 147 days (post-infection day 87). B Expression of NRIP in GAS muscles of AAV-NRIP treated SOD1 G93A mice. Protein extracts from the GAS muscles were collected at the end stage of the experiment and assessed for the expression of exogenous NRIP (Flag-NRIP) and GFP. The endogenous NRIP NRIP was detected by the anti-NRIP antibody. The asterisk indicated the Flag-NRIP expression; the arrowhead indicated the endogenous NRIP expression. GAPDH was the loading control. AAV-GFP group, N = 3 mice; AAV-NRIP group, N = 3 mice. C NRIP expression in muscles from AAV-GFP treated or AAV-NRIP treated SOD1 G93A mice. Immunofluorescence (IF) analysis for exogenous NRIP (right) expression with an anti-Flag antibody and GFP (left) expression with the anti-GFP antibody in GAS muscles. D NRIP retrograde expression in cholinergic neurons of the spinal cord from AAV-GFP treated or AAV-NRIP treated SOD1 G93A mice. IF stain for exogenous NRIP expression in the spinal cord. The Flag-NRIP expression was detected using an anti-Flag antibody (red), and the cholinergic neurons were stained using an anti-ChAT antibody (green). ChAT-positive neurons expressing Flag-NRIP are indicated by arrows. DAPI was the nuclear counterstain. Scale bars: 100 μm