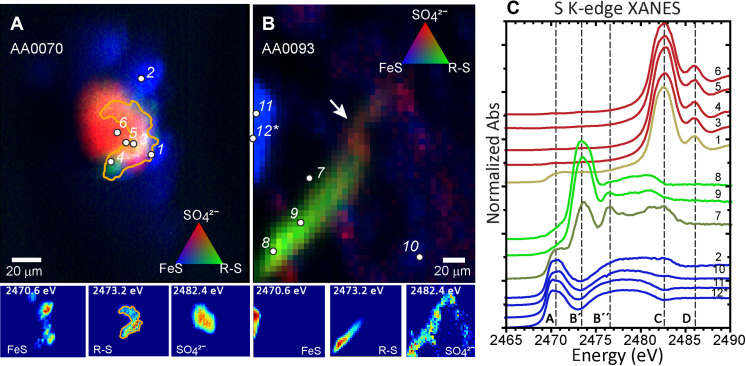
Fig. 1. Stacked multiple-energy x-ray fluorescence maps collected across the sulfur absorption edge reveals two thiol-rich regions identified in Ryugu particles A0070 and A0093.
(A) The thiol (in green) forms a partial rim, about 10 μm wide around a calcium sulfate grain (in red). The rim is surrounded by smaller monosulfide grains (in blue). (B) The thiol forms a (60 μm by 20 μm) filamentous structure that fades into a methionine sulfoxide and then sulfate-rich region (shown at arrow). This exists in a phyllosilicate-rich region in close proximity to a monosulfide grain. (C) Sulfur K-edge XANES were collected at spots of interest [points 1 to 12 shown in (C)], and normalized spectra are shown. Vertical dashed lines in the plots of spectra show the following: (A) inorganic monosulfides (Fe1−xS) pyrrhotite/troilite; (B′) cysteine as a representative thiol (R-SH); (B″) methionine sulfoxide (R-(SO)-R; (C) characteristic S6+ sulfate (SO42−); (D) secondary peak characteristic of Ca-sulfate (CaSO4) such as gypsum. XANES fits are shown in table S1.