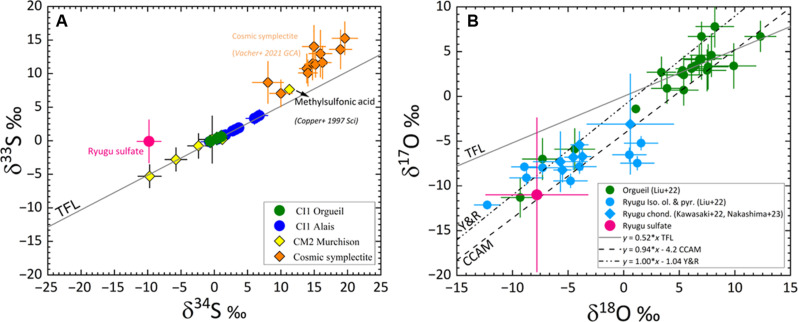
Fig. 3. Oxygen and sulfur isotopic compositions of the Ca-thiosulfate grain in A0070.
(A) Three-sulfur isotope plot showing the sulfur isotopic composition of sulfides in several CC meteorites, cosmic symplecties (25), methylsulfonic acid (16), and the thiol- and sulfate-bearing composite grain identified in Ryugu particles A0070 with a Δ33S = 5 ± 2‰ (1σ). A normal sulfur isotopic fractionation process means that a change in mass of 2 amu (34S -32S) for δ34S is accompanied by a 1 amu for δ33S. This results in an observed factor of 2 for a mass-dependent fractionation owing to chemical and physical processes. Any deviation from it is considered “isotopically anomalous” or mass independent in nature, which is the case for the Ca-thiosulfate grain in the Ryugu particle A0070. (B) The O isotopic composition of Ryugu Ca-thiosulfate grain A0070-Sul is consistent with that measured in a few points in Orgueil as well as isolated olivines and pyroxenes and chondrule fragments in Ryugu (22–24) The Terrestrial Fractionation Line (TFL), Young and Russell (Y&R) line, and CCAM line are also shown. The TFL is derived from measurements of terrestrial samples falls along a line with slopes (~0.5). The CCAM line is derived from analyses of refractory inclusions in CV3 CC Allende has a slope of 0.94. It is used for assessing the magnitude by which planetary and asteroidal materials depart from the three-isotope distribution of Earth’s oxygen reservoir. Young and Russell (61) have proposed that a line of exactly slope 1 defines the primordial variation in oxygen isotopes in the protosolar disk. This primitive oxygen isotope composition was subsequently modified by later parent body processes to form the CCAM line. Data are in table S11.