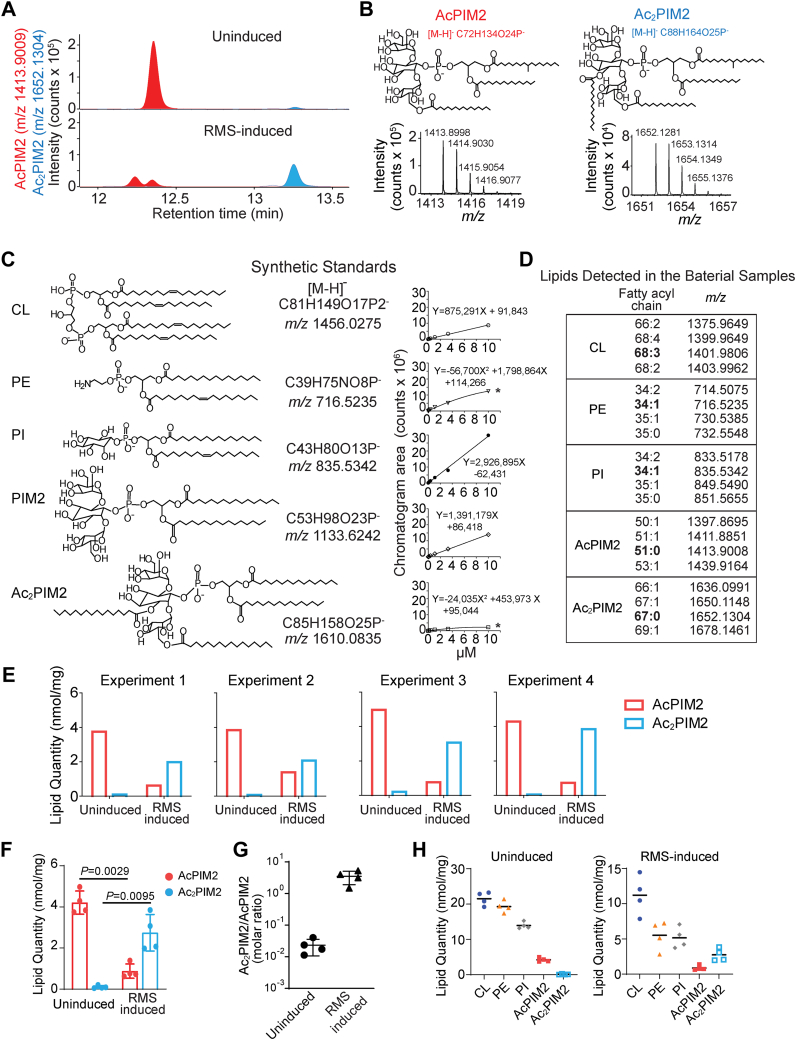
Fig. 7.
Quantification of AcPIM2 and Ac2PIM2 by HPLC-MS. A: Lipid extracts from wet pellets of log phase cells grown in the standard growth medium were analyzed by negative-mode, reversed phase HPLC-Q-TOF-MS in biological quadruplicates. The ion chromatograms of the most abundant species in AcPIM2 (m/z 1413.8998) and Ac2PIM2 (m/z 1652.1281) lipid classes were detected in uninduced and RMS-induced conditions, respectively. A representative chromatogram from one replicate is shown. B: The mass spectrum of the most abundant AcPIM2 and Ac2PIM2 shown in panel A with structures based on the literature. C: A series of known concentrations of synthetic compounds, CL, PE, PI, PIM2, and Ac2PIM2 were analyzed by HPLC-MS to generate standard curves using linear or nonlinear equations for curve fitting as indicated. ∗the nonlinear fitting results were verified by the linear fitting results with logarithmic scale conversion of both x- and y-axis shown in Supplemental Fig. S1. D: Four major lipid species in each phospholipid class were listed, and the most abundant species was indicated in bold. E: The concentration of AcPIM2 or Ac2PIM2 in each condition was converted from the chromatogram area shown in (A) to nmol/mg lipid based on the external standard curve fitting. The quantities of AcPIM2 were estimated by averaging the amounts calculated using both PIM2 and Ac2PIM2 standard curve fitting. F: Four experiments in panel E were combined for the statistical analysis using the paired two-tailed Student's t test. G: The comparison of Ac2PIM2 to AcPIM2 molar ratio in two cellular conditions calculated from panel E. H: The phospholipid abundance was estimated in nmol per mg lipid using all lipid species listed in panel D, based on external standard curve fitting.