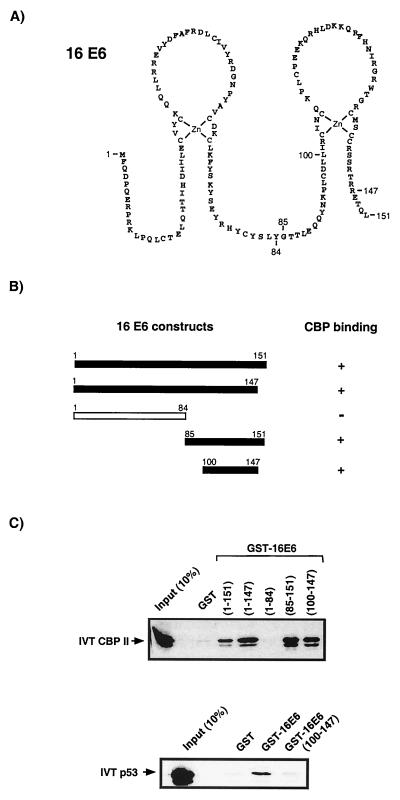
FIG. 3.
Mapping of a 16E6 region involved in the interaction with CBP. (A) Amino acid sequence of the 16E6 protein. The two zinc finger structures are hypothetical, since they have not been based on spectroscopic methods but are supported by the strict conservation of eight cysteine residues in all HPV E6 proteins, as well as by the stoichiometric binding of zinc ions by E6 molecules (7, 21). Indicated are the numbers of the amino acid residues which mark the start or end points of 16E6 fragments used in interaction studies. (B) Schematic representation of GST-E6 fusion constructs used in micro-affinity column assays. (C) Interaction experiments define a region between 16E6 residues 100 to 147 as sufficient for the binding of CBP. This same region is not able to bind p53, however, indicating that p53 and CBP binding are dependent on different 16E6 domains.