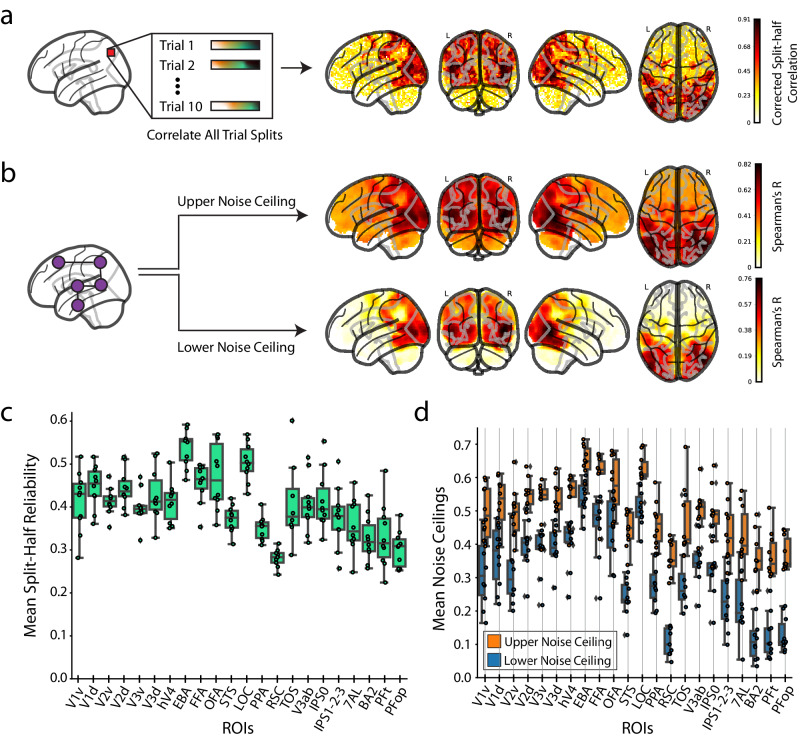
Fig. 3. Whole-brain and ROI reliability after response modeling.
a Whole-brain single-subject split-half reliability analysis: We perform a voxelwise split-half reliability analysis and present the voxels with Spearman-Brown corrected values that pass the reliability criteria (p < 0.05, permutation-based, one-sided) for subject 1. b Whole brain searchlight noise-ceiling analysis: We estimate the upper and lower noise-ceilings across the whole brain for a representative subject (subject 1) from a searchlight representational dissimilarity analysis (RSA). c ROI-based group split-half reliability: For each of the 22 ROIs, we present the mean split-half reliability across participants from the voxels passing the reliability criteria. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. d ROI-based group searchlight noise ceilings: For each of the 22 ROIs, we calculate the upper (orange) and lower (blue) noise ceilings across participants. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. The box plots encompass the first and third data quartiles and the median (horizontal line). The whiskers extend to the minimum and maximum values within 1.5 times the interquartile range, and values falling outside that range are considered outliers (denoted by a diamond). The overlaid points show the value at each observation (n = 10 for all ROIs except transverse occipital sulcus (TOS, n = 8) and retrosplenial cortex (RSC, n = 9)). The brain responses used for the reliability analyses are the beta values averaged over TRs 5-9 (the peak of the BOLD signal) from the testing set.