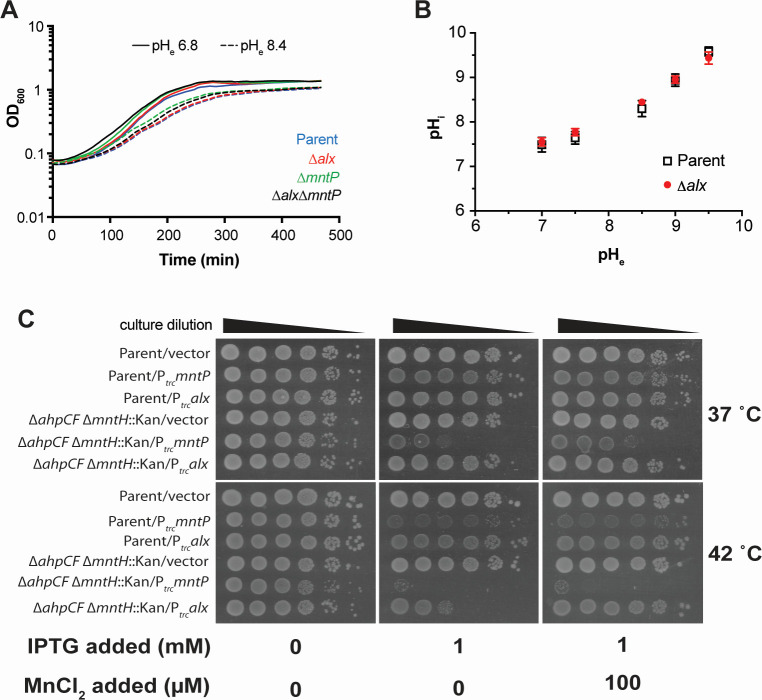
Fig 3.
Effect of an increased external pH and combined effect of oxidative stress and perturbed cellular manganese levels on cellular growth. (A) Growth of the parent strain (MC4100) and its derivatives (∆alx::Kan derivative, RAS31; ∆mntP::Kan derivative, RAS32, and ∆alx ∆mntP::Kan derivative, RAS42) in LBK media pH 6.8 or pH 8.4. (B) Cytoplasmic pH (pHi) measured in the parent strain (MC4100) and its ∆alx::Kan derivative (RAS31) expressing pHluorin in M63A media of varying pH. Each plotted value of pHi in the graph with SEM is an average of three biological replicates of the experiment. (C) The spotting assay of tenfold serial dilutions (left to right) of overnight-grown cultures of parent strain (MC4100) and its ∆ahpCF ∆mntH::Kan derivative (RAS95) each bearing an empty vector (pHYD5001) or the same vector expressing MntP (pRA29) or Alx (pRA27) from Ptrc promoter. The serial dilutions were spotted on the surface of LB agar containing the appropriate concentration of ampicillin, MnCl2, and IPTG. Plates were imaged after an incubation at 37 or 42°C for 14 hours. The data shown are representative of three biological replicates of the experiment.