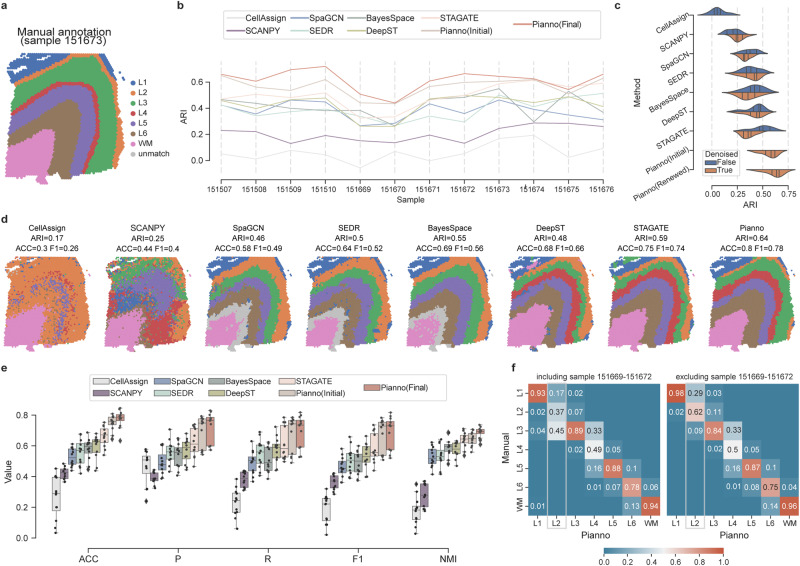
Fig. 2. Evaluation of Pianno’s performance in cortical architecture reconstruction.
a Manual annotation of anatomical structures, including cortical layers (L1-L6) and white matter (WM), within a representative dlPFC section (sample 151673). b Adjusted rand index (ARI) assessing the concordance between labels predicted by different methods and the manual annotation. The black lines inside the violin indicate the quartiles. c Comparison of dlPFC samples (n=12) with and without SAVER preprocessing. d Cortical architecture segmentation by CellAssign24, SCANPY25, SpaGCN8, SEDR9, BayesSpace7, DeepST10, STAGATE11, and Pianno. The clusters identified by spatial clustering approaches were mapped to the manual annotation using Kuhn-Munkres algorithm59. e Boxplot summarizing annotation metrics across all 12 samples. The box bounds the interquartile range (IQR) divided by the median, with the whiskers extending to a maximum of 1.5 × IQR from the box, and values beyond the whiskers are considered outliers, marked with diamonds. ACC: accuracy; P: macro-averaging precision; R: macro-averaging recall; F1: macro-averaging F1-score; NMI: normalized mutual information. f Confusion matrix normalized by column depicting the comparison between Pianno and manual annotations in all 12 samples (including sample 151669–151672, left) and 8 samples (excluding sample 151669–151672, right). Diagonal values in the matrix represent the precision of each layer. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.