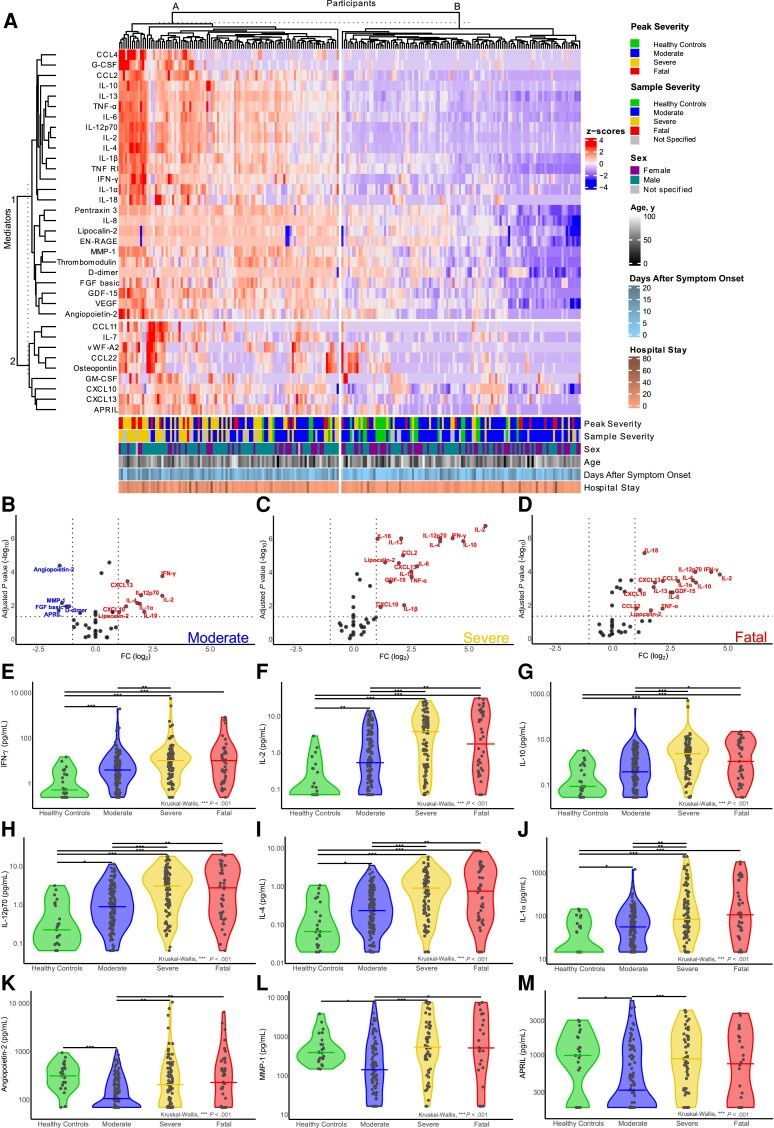
Figure 1.
COVID-19 severity was associated with clusters of elevated inflammatory markers in the nasal mucosa. A, K-means clustered heatmap of 35 cytokines and chemokines in the nasal mucosa of healthy controls (n = 25) and patients hospitalized with COVID-19 (n = 215). Annotations provide participant peak severity (peak severity), severity at the time of sample collection (sample severity), sex, age, duration of symptoms at the time of sample collection (days after symptom onset), and total duration of hospital stay (hospital stay) in days. B–D, Nasal cytokine and chemokine levels in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 (n = 274) shown as volcano plots relative to healthy controls for (B) moderate, (C) severe, and (D) fatal peak COVID-19 severity groups. Data shown are −log10 transformed false discovery rate adjusted Wilcoxon rank-sum P values (horizontal line at cutoff ≥.05) plotted against log2 fold changes (vertical lines at cutoffs ≤ −2 and ≥2) for nasal samples taken at 0–20 days after symptom onset. E–M, Individual cytokines and chemokines of particular interest in each COVID-19 peak-severity group and healthy controls: (E) IFN-γ, (F) IL-2, (G) IL-10, (H) IL-12p70, (I) IL-4, (J) IL-1α, (K) angiopoietin-2, (L) MMP-1, and (M) APRIL. Group median levels are shown as lines and significance levels determined using Kruskal-Wallis tests with Dunn's P value correction. B–M, Data from the first time point per participant are shown. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001. Abbreviations: APRIL, A proliferation-inducing ligand; COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; FC, fold change; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; G-CSF, granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor; GDF-15, growth differentiation factor 15; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; IL, interleukin; IFN-γ, interferon-γ; MMP-1, matrix metalloproteinase-1; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.