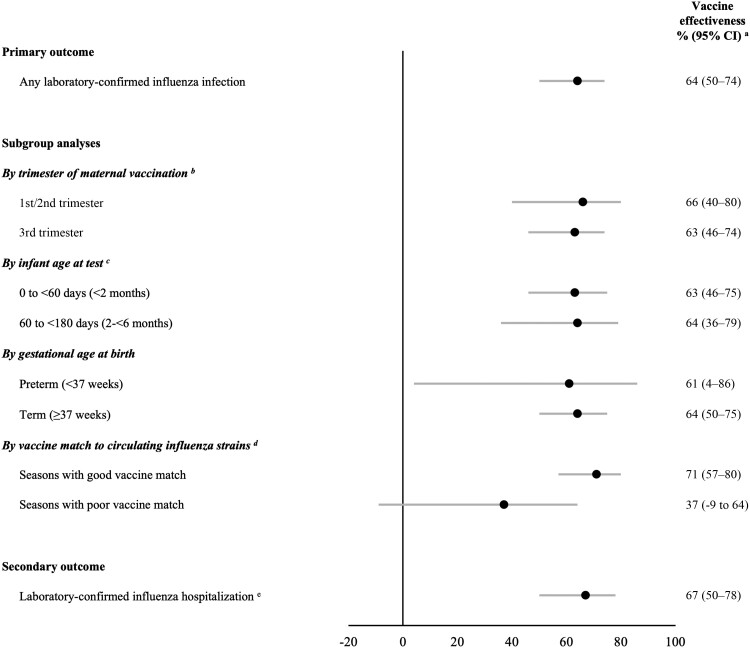
Figure 3.
Estimated effectiveness of maternal influenza vaccination during pregnancy against laboratory-confirmed influenza among infants <6 months of age (additional data provided in Supplementary Table 5). aVaccine effectiveness was estimated as 1 minus the adjusted odd ratio, comparing the odds of maternal influenza vaccination during pregnancy among test-positive infant cases relative to test-negative infant controls. Odds ratios were adjusted for infant age at test, season of birth, prenatal care adequacy, neighborhood income, and influenza season (with the exception of the subgroup analysis by infant age at test, for which odds ratios were adjusted for season of birth, prenatal care adequacy, neighborhood income, and influenza season). bResults for first and second trimester vaccinations were combined due to small cell counts. cResults for 60 to <120 days and 120 to <180 days were combined due to small cell counts. dInfluenza vaccines in 2014–2015 and 2017–2018 were not considered well matched against circulating influenza strains (see Supplementary Table 4). eCase specimens were limited to those collected during an admission to a hospital ward or intensive care unit. Controls were infants who tested negative for influenza in any clinical setting. Abbreviation: CI, confidence interval.