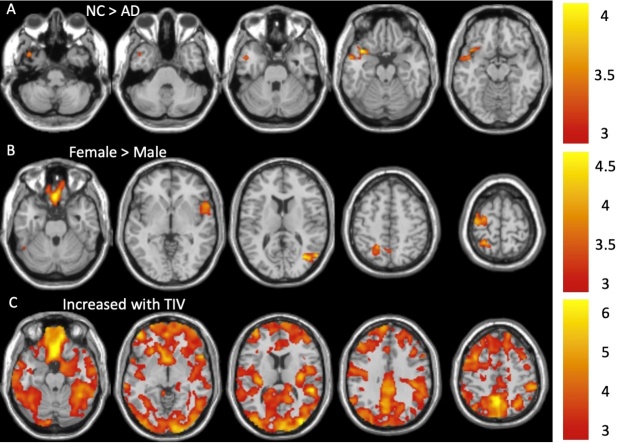
Figure 2.
The AD group had significant GMV decreases (A) in the temporal pole cluster (Cluster 1) compared with the NC group after adjusting for age, gender, and TIV effects. Females showed significantly larger GMVs (B) in the rectus (Cluster 2), fusiform (Cluster 3), rolandic operculum and inferior frontal (Cluster 4), middle temporal (Cluster 5), precuneus and superior parietal (Cluster 6), and precentral (Cluster 7) regions after adjusting for age and TIV effects. Larger GMVs were associated with larger TIVs (C) in almost the entire brain (Cluster 8) after adjusting for age and gender effects. The color bars show the range of t-values.