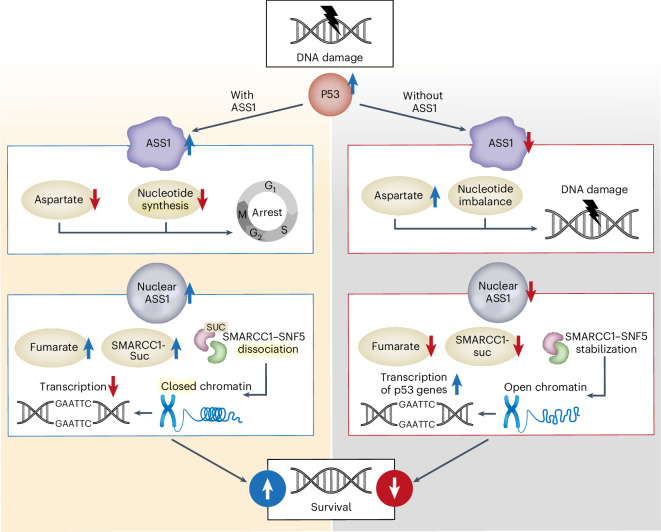
Fig. 5. Suggested model for the requirement of ASS1 in the p53-response to DNA damage.
In cells expressing ASS1, upon DNA damage, p53 levels are elevated, upregulating the expression of ASS1. ASS1 acts as a metabolic cell cycle checkpoint in the cytosol by regulating nucleotide levels. In the nucleus, ASS1 regulates fumarate levels needed for the succination of SMARCC1. Upon succination, there is a dissociation of SMARCC1 from SNF5, decreasing chromatin accessibility and p53-related transcription. In the absence of ASS1, there is an increase in cytosolic aspartate levels, leading to unregulated nucleotide synthesis and promoting DNA damage. In the nucleus, loss of ASS1 expression leads to increased SMARCC1–SNF complex, higher chromatin accessibility and transcription of p53 genes. Upwards and downward arrowheads indicate an increase or decrease, respectively. The scheme was created by Weizmann Graphics team.