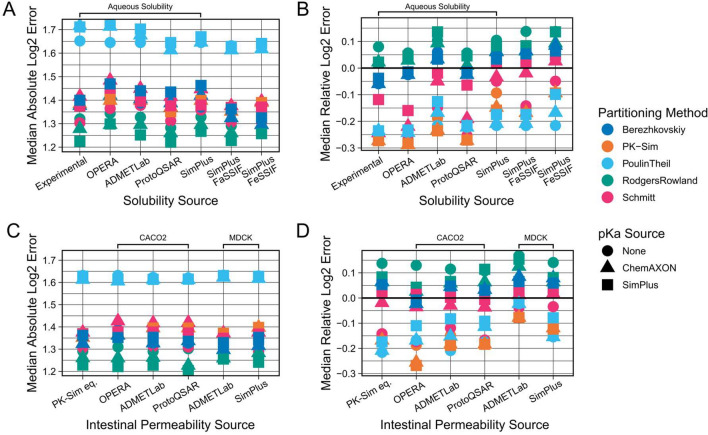
Fig. 5.
Comparison of predictive performances of different solubility and intestinal permeability prediction sources (step 3). Combinations of all available parameterisation sources were evaluated against the collected PO dataset (dissolved formulations). Results shown were generated using benchmark values for parameterisation of other parameters, i.e., in vivo plasma clearances, in vitro fraction unbound values and the mean of the two previously determined best lipophilicity prediction tools (LogD and LogMA Bayer) as lipophilicity values. The top row shows the Median Absolute Log2 Errors (A) and the Median Relative Log2 Errors (B) for different solubility prediction methods. The bottom row shows the Median Absolute Log2 Errors (C) and the Median Relative Log2 Errors (D) for different intestinal permeability prediction methods. For comparison of solubility predictions, the intestinal permeability values used were the PK-Sim internal equation values (PK-Sim eq.). For comparison of intestinal permeability sources, the solubility values used were SimPlus FaSSIF values. Results for the PK-Sim internal equation were generated with the Bayer LogMA predictions. Intestinal permeability predictions are either CACO2 or MDCK permeability predictions