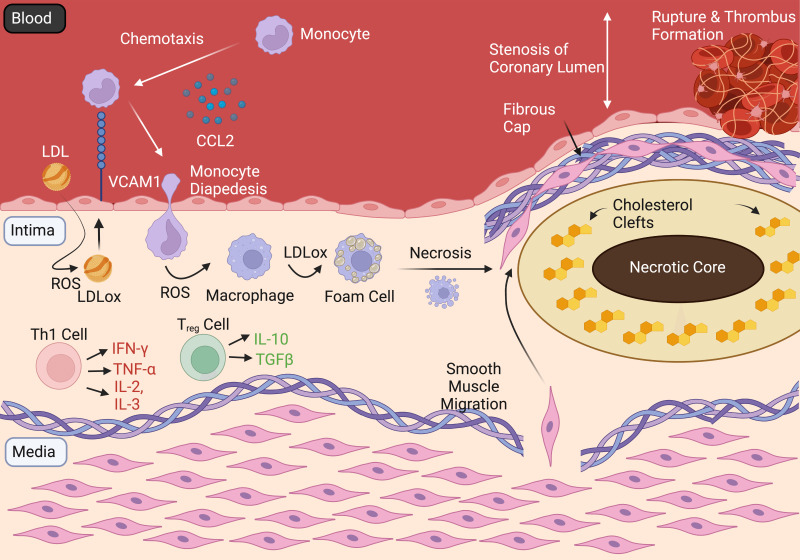
Fig. 1.
Pathogenesis and Complications of IHD. Figure summarising the development and progression of the atherosclerotic plaque, which obstructs the coronary lumen and if unstable—can rupture, with subsueqent thrombus formation occluding the affected coronary artery—resulting in acute coronary syndromes. LDL, low density lipoprotein; VCAM1, vascular cell adhesion molecule 1; CCL2, chemoattractant protein 1; ROS, reactive oxygen species; LDLox, oxidised LDL; IFN-Y, interferon gamma; TNF-, tumour necrosis factor alpha; IL-2, interleukin 2; IL-3, interleukin 3; IL-10, interleukin 10; TGF, transforming growth factor beta; Th1, T helper type 1; , regulatory T cell.