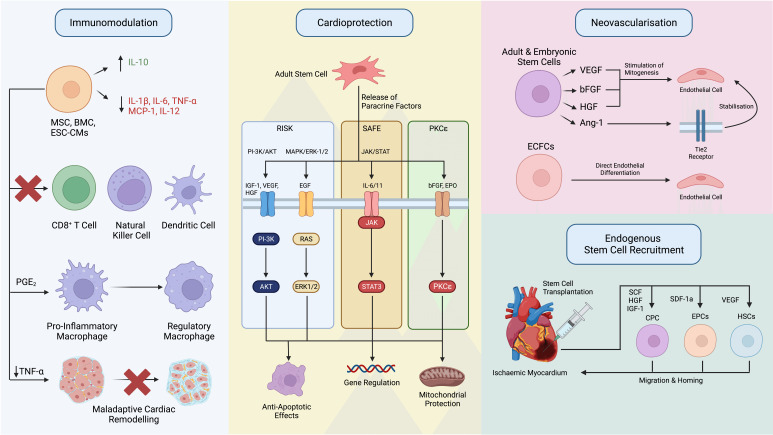
Fig. 4.
Stem Cell Mechanisms for Cardiac Repair. Summary of the proposed mechanisms for cardiac repair by transplanted stem cells. Stem cells secrete various factors with a paracrine effect on other cells promoting cardioprotection, neovascularisation, immunomodulation and endogenous stem cell activation, along with an autocrine feedback effect to enhance their survival. IL-10, interleukin 10; IL-1, interleukin one beta; IL-6, interleukin 6; TNF-, tumour necrosis factor alpha; MCP-1, monocyte chemoattractant protein 1; IL-12, interleukin 12; PGE2, prostaglandin E2; RISK, reperfusion injury salvage kinase; SAFE, surviving factor enhancement; PKC, protein kinase C epsilon; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; ERK, extracellular signal-related kinase; JAK, janus tyrosine kinase; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor-1; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; EGF, epidermal growth factor; IL-11, interleukin-11; bFGF; basic fibroblast growth factor; EPO, erythropoietin; RAS, rat sarcoma virus protein; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; Ang-1, angiopoietin-1; Tie2, tyrosine kinase with immunoglobulin-like loops and epidermal growth factor homology domains-2; SCF, stem cell factor; CPC, cardiac progenitor cell; SDF-1, stromal cell-derived factor 1-alpha; EPC, endothelial progenitor cell; HSC, haemopoietic stem cell; ECFC, endothelial colony-forming cell.