Table 3.
Difference between multiglandular parathyroid disease, solitary adenoma and carcinoma using clinical and laboratory parameters and imaging.
| Clinico-Radio-Pathological Features | Multiglandular Parathyroid Disease | Solitary Parathyroid Adenoma | Parathyroid Carcinoma |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | Variable, usually >50 years Early onset in hereditary forms |
>50 years | Around 50 years Early onset in HPJT and familial forms |
| Gender | Females | Females | Equal gender incidence |
| Clinical manifestations | Symptoms of primary hyperparathyroidism and those associated with familial syndromes and MEN (when present) |
Asymptomatic Symptoms of primary hyperparathyroidism |
Symptoms of primary hyperparathyroidism especially simultaneous bone and renal disease (functional), HPJT, symptoms associated with familial syndromes and MEN (when present), palpable neck nodes, hoarseness of voice due to RLN palsy |
| Laboratory parameters | Serum calcium: <13 mg/dL Serum PTH: Mildly to severely elevated Hypocalciuria in FHH |
Serum calcium: <13 mg/dL Serum PTH: Mildly to moderately elevated |
Serum calcium: >14 mg/dL Serum PTH: more than three times upper limit of normal |
| Imaging features |
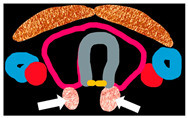
Imaging morphology Bilaterally enlarged (may be asymmetric) homogeneous polar glands adjacent to thyroid on US, 4DCT, 4DMRI Imaging characteristics Intense homogeneous enhancement on CEUS. |
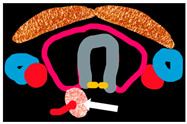
Imaging morphology Well circumscribed homogeneous oval/oblong-shaped polar lesion adjacent to thyroid with feeding vessel sign on US and 4DCT. Imaging characteristics Hypoechoic on US Early peripheral enhancement and central washout in the delayed phase on CEUS. Hypodense to thyroid on non-contrast scan, usually hyper-enhancing in the arterial phase with feeding vessel sign and washout in the venous phase on 4DCT. Homogeneous or marbled T2 hyperintensity lesion with fluid fat interface on out-of-phase imaging between thyroid gland and PA, and rapid post-contrast enhancement on 4DMRI. |
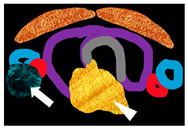
Imaging morphology Large (>3 cm) heterogeneous lesion, irregular shape, epicentred adjacent to thyroid with lobulated margins infiltrating thyroid and surrounding structures, short/long-axis ratio >0.76, long axis diameter >30 mm, presence of central and peripheral vascularity, and intratumoural calcification along with metastatic neck nodes on US, 4DCT, 4DMRI. Parathyroid carcinoma is differentiated from PA based on morphological features only. |
| Functional imaging | Technetium(99mTc) Sestamibi: Focal uptake over bilateral upper and lower poles of thyroid lobes in the early phase, with persistent uptake in the delayed phase. |
Dual-energy CT 4DCT: Differentiation of parathyroid lesion from thyroid tissue using non-contrast 40-keV virtual monoenergetic images for parathyroid lesions which are isodense to thyroid in the arterial and venous phases. 99mTc Sestamibi: Early phase shows focal increased radiotracer uptake near the superior/inferior polar region of thyroid, with persistent uptake in the delayed phase. |
FDG-PET CT: Distant metastasis No specific characteristics on Technetium (99mTc) Sestamibi |
| Pi |
|
|
|
PA: parathyroid adenoma, HPJT: hyperparathyroidism jaw-tumour syndrome. MEN: multiple endocrine neoplasia, RLN: recurrent laryngeal nerve, PTH: primary hyperparathyroidism, FHH: familial hypocalciuric hypercalcaemia, US: ultrasound, CEUS: contrast-enhanced ultrasound, 4DCT: four-dimensional computed tomography, 4DMRI: four-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging, FDG-PET: fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography.
