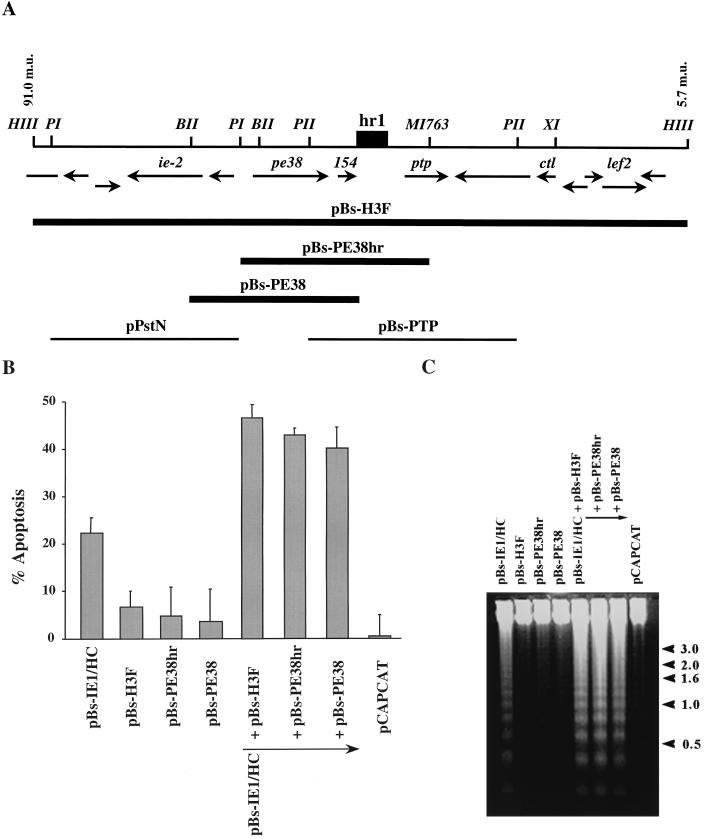
FIG. 1.
Subclones of the AcMNPV HindIII-F fragment including PE38 augment IE1-induced apoptosis. (A) Location and direction of ORFs within the HindIII-F fragment between 91.0 and 3.4 m.u. are those determined by Ayres et al. (2) and are indicated by arrows below a physical map with key restriction enzymes. A dark box indicates the position of the homologous region hr1. Restriction sites are abbreviated as follows: HIII, HindIII; BII, BglII; BHI, BamHI; PI, PstI; XI, XhoI; MI763, MscI763. Solid lines indicate plasmids, which augment IE1-induced apoptosis. Thin lines at the bottom indicate clones of other portions of the region which did not augment IE1-induced apoptosis. (B) Percentage of SF-21 cells undergoing apoptosis by 18 h posttransfection with pBs-IE1/HC and different subclones of the AcMNPV HindIII-F fragment. pCAPCAT was used as a negative control of apoptotic activity (0% of apoptosis) and to balance total plasmid DNA levels to 2.0 μg of plasmid DNA in each transfection. The data represent the averages of two or more experiments, and standard errors are indicated. (C) DNA fragmentation pattern of transfected cells. Total cellular DNA was extracted from SF-21 cells cotransfected with the indicated plasmids and subjected to 1.2% agarose gel electrophoresis. DNA was visualized by ethidium bromide staining. The pCAPCAT-transfected cells served as a negative control for apoptosis. The positions of DNA molecular weight markers (sizes in kilobase pairs) are indicated at the right by arrowheads.