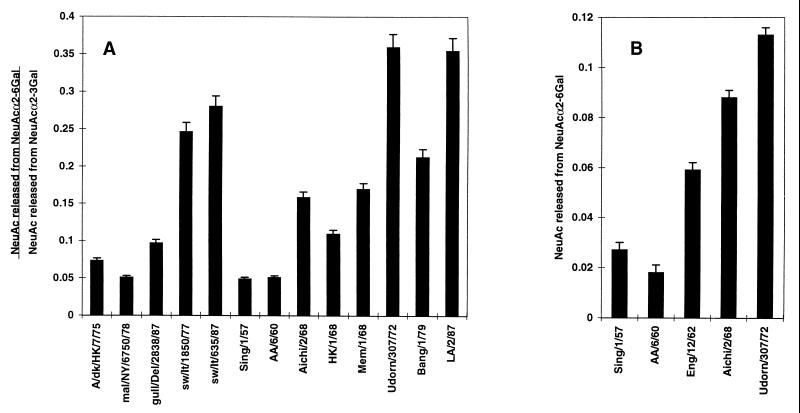
FIG. 1.
NeuAcα2-6Gal substrate specificities of avian, swine, and human virus N2 NAs. Virus strains were compared for their ability to release sialic acid from sialyllactoses containing either the NeuAcα2-3Gal or the NeuAcα2-6Gal linkage. (A) Ratio of sialic acid released from a 0.1 mM concentration (50 μl) of each substrate (NeuAcα2-6Gal and NeuAcα2-3Gal) by 10.0 mU of viral NA per ml. (B) Absolute amount of sialic acid released from a 0.1 mM concentration (50 μl) of NeuAcα2-6Gal-containing sialyllactose by 100.0 mU of NA per ml in 30 min at 37°C. The amount of released sialic acid was determined by the periodate-thiobarbituric acid assay (22) and reported as the absorbance of the colored chromophore derivative at 549 nm.