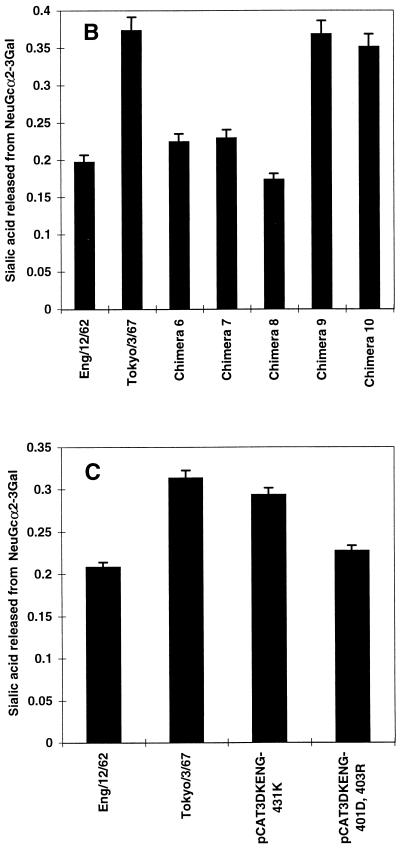
FIG. 4.
Determination of amino acid residues contributing to NeuGc specificity. (A) Chimeras 6 to 10, in which the sequences of A/England/12/62 N2 NA (□; pCAT3DKENG62NASAP) were replaced with the equivalent sequences of A/Tokyo/3/67 N2 NA (■; pCAT3TOKYO67NASAP), were generated as described in the legend to Fig. 2 for chimeras 1 to 5. Parental NAs and chimeras 6 to 10 (B) or A/England/12/62 mutant constructs containing amino acid substitutions N401→D and W403→R (pCAT3DKENG-401D,403R) and Q431→K (pCAT3DKENG-431K) (C) were expressed as described in the legend to Fig. 2. Cell-expressed NA (0.5 mU) was incubated with 0.1 mM GM3 ganglioside substrate containing NeuAc or NeuGc in the presence of 0.1% SDC for 30 min at 37°C. The amount of sialic acid released from NeuGcα2-3Gal was determined as described in the legend to Fig. 1.