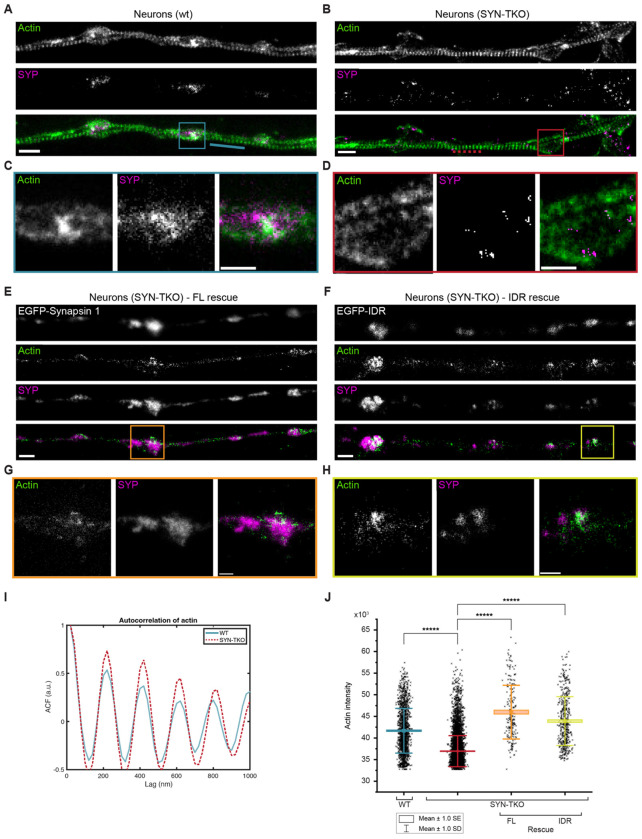
Figure 5: Synaptic vesicle condensates are necessary for concentrating actin at the presynaptic boutons.
A, B. Two-color super-resolution STED images of hippocampal neurons (14 DIV) from (a) wild-type and (b) synapsin triple knockout neurons stained with StarRed-phalloidin and anti-synaptophysin (Star580). Scale bar, 1 μm.
C. Magnified region from (a) showing a cohort of synaptic vesicles (anti-synaptophysin) colocalizing with actin (StarRed-phalloidin).
D. Magnified region from (b) indicating a more dispersed signal of SVs (anti-synaptophysin) lacking the colocalization with actin (StarRed-phalloidin). Scale bar, 0.5 μm.
E, F. Representative images of synapsin triple knockout neurons rescued with (e) full-length EGFP-synapsin 1 or (f) EGFP-synapsin 1 IDR and stained with StarRed-phalloidin and anti-synaptophysin (Star580). Scale bar, 1 μm.
G, H. Magnified regions from (e) and (f), respectively, showing colocalization of SVs with actin. Scale bar, 0.5 μm.
I. Autocorrelation of the actin signal along the axons (StarRed-phalloidin; see dotted/while lines in the images in a and b) indicates that actin rings remain unaltered in the absence of synapsins.
J. Actin enrichment in synaptic vesicle cohorts defined as an intensity signal of actin channel within regions positive for synaptophysin (wild-type and synapsin triple knockout) or both synaptophysin and EGFP (in rescue experiments).