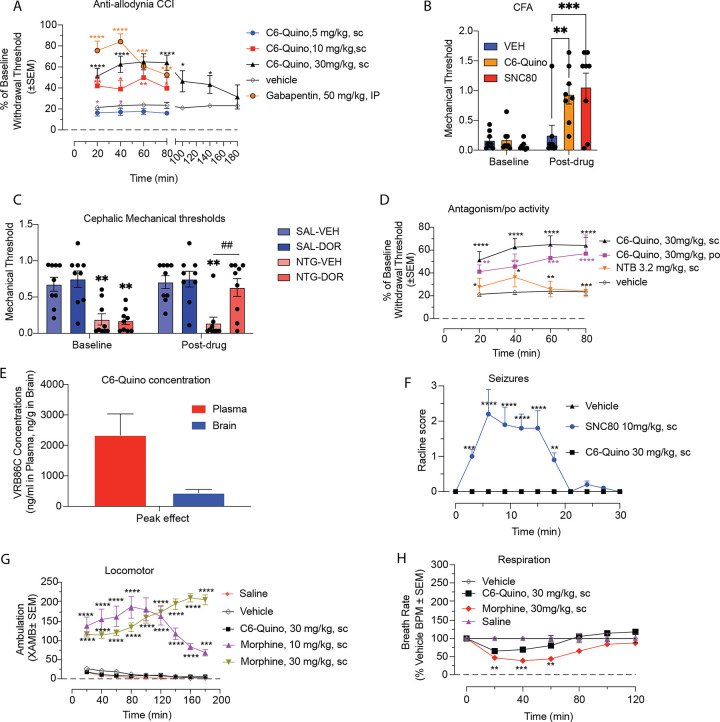
Figure 5. In vivo characterization of C6-Quino in chronic pain states.
A) C6-Quino displays robust antiallodynic effect at both 10 mg/kg and 30 mg/kg dose similar to gabapentin at 50 mg/kg dose in the chronic constriction injury (CCI) model of neuropathic pain (Two-way RM ANOVA: treatment x time: F(12,144)=3.57, p=0.0001) and B) C6-Quino (30 mg/kg, sc) shows comparable anti-hyperalgesic effects to SNC80 (10mg/kg, sc) in the Complete Freund’s Adjuvant (CFA) model of inflammatory pain ((2-way ANOVA, p=0.0066 timeXtreatment interaction; Holm-Sidak post-hoc analysis **p=0.0025 comparing VEH-C6-Quino at Post-Drug time, ***p=0.006 comparing VEH-SNC80 at Post-Drug time). C) C6-Quino (30mg/kg, sc) completely reversed cephalic allodynia in the nitroglycerin model of chronic migraine (3-way ANOVA, p<0.05 timeXtreatmentXdrug interaction; Holm-Sidak post-hoc analysis **p<0.01 compared to SAL-VEH, ##p<0.01 compared to NTG/VEH). D) C6-Quino is effective in both po. and sc. regimes at 30 mg/kg dose and its effect can be antagonized with NTB in the chronic constriction injury (CCI) model (Two-way RM ANOVA: treatment x time: F(12,129) =2.88, p=0.002). E) C6-quino shows reasonable brain and plasma exposure in pharmacokinetic assays in mice.). F) C6-Quino does not cause convulsions at 30 mg/kg dose unlike the full agonist, SNC80 at 10 mg/kg (sc.) (Two-way RM ANOVA: treatment x time: F(20,231) =6.99, p<0.0001). G) C6-Quino, unlike morphine, does not produce hyperlocomotion (Two-way RM ANOVA: treatment x time: F(32,567) =7.37, p<0.0001. H) Morphine causes significant decrease in respiration rate at 30 mg/kg. C6-Quino did not lead to significant respiratory depression at 30 mg/kg,sc when compared with vehicle. Respiratory rate. Mice were administered either vehicle (n = 12), morphine (30 mg/kg, sc; n = 12), or C6 Quino (30 mg/kg, sc; n = 12), and the breath rates was measured every 20 min for 120 min. Morphine administered sc caused reduction in the breath rate with respect to saline at 20 min (**p = 0.0029), 40 min (***p = 0.0004) and 60 min (**p = 0.0014) post drug administration. C6-Quino (30 mg/kg, sc) was not significantly different from vehicle control as determined by 2-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple-comparison test.