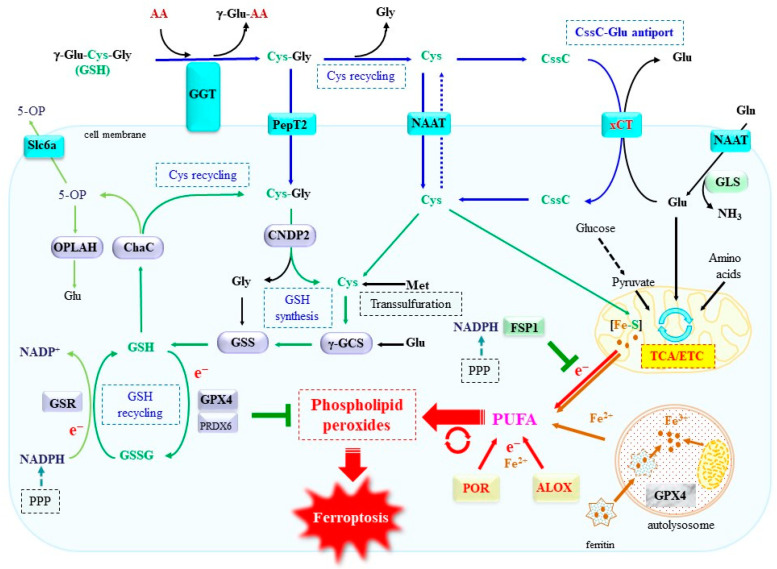
Figure 1.
Principle pathways for induction of and protection from ferroptosis. Free iron mainly comes from either ferritinophagy or mitochondrial iron, but also originates from iron-containing enzymes. These components may also become the source for radical electrons to initiate lipid peroxidation. Cys availability determines the cellular levels of glutathione, which supports GPX4 in the protection against lipid peroxidation. Part of the central metabolic pathways discussed in the text are also depicted. AA, amino acid; γ-Glu-AA, γ-glutamyl amino acid; CssC, cystine; PepT2, dipeptide transporter; PPP, pentose phosphate pathway; 5-OP, 5-hydroxy proline; Slc6a, 5-oxoproline transporter; TCA, tricarboxylic acid cycle; ETC, electron transport chain; GSR, glutathione reductase; GLS, glutaminase; FSP1, ferroptosis-suppressor protein 1; POR, cytochrome P450 reductase; ALOX, arachidonate-specific lipoxygenase.