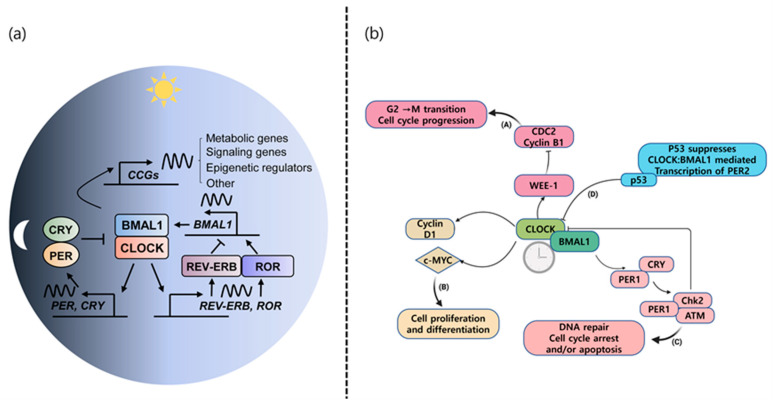
Figure 1.
(a) This autoregulatory feedback loop cycles between the CLOCK/BMAL1 transcriptional activator complex and its repressors (PER/CRY, REV-ERBα) or activators (RORα/β) to constitute the molecular clock oscillator that drives the expression of multiple clock-controlled genes (CCGs), such as metabolic genes, signaling genes, and epigenetic regulators. Reproduced from Ref. [38] (CC By 4.0). (b) Molecular interaction between the circadian core clock and cell cycle components. The CLOCK:BMAL1 complex transcriptionally activates genes containing E-box regulatory elements in their regulatory regions, such as clock genes and cell cycle genes. (A) The CLOCK:BMAL1 complex directly controls the transcription of the cell cycle-related gene Wee-1 which contains three B-boxes in its promoter and encodes a protein kinase that inactivates the CDC2/Cyclin B1 complex, thus regulating G2-M transition and cell cycle progression. (B) Transcriptional activation of the genes encoding Cyclin D1 and C-MYC by CLOCK:BMAL1 affects cell proliferation and differentiation. (C) PER1 can complex with the ATM kinase and the checkpoint kinase Chk2, thus impinging upon DNA repair, cell cycle arrest, and/or apoptosis. (D) Both physiological and stress-induced p53 binds to the p53 response element in the PER2 promoter, which overlaps with the BMAL1/CLOCK-binding site, thereby inhibiting the CLOCK:BMAL1-mediated transcription of PER2. Reproduced from Ref. [14] (CC By 4.0).