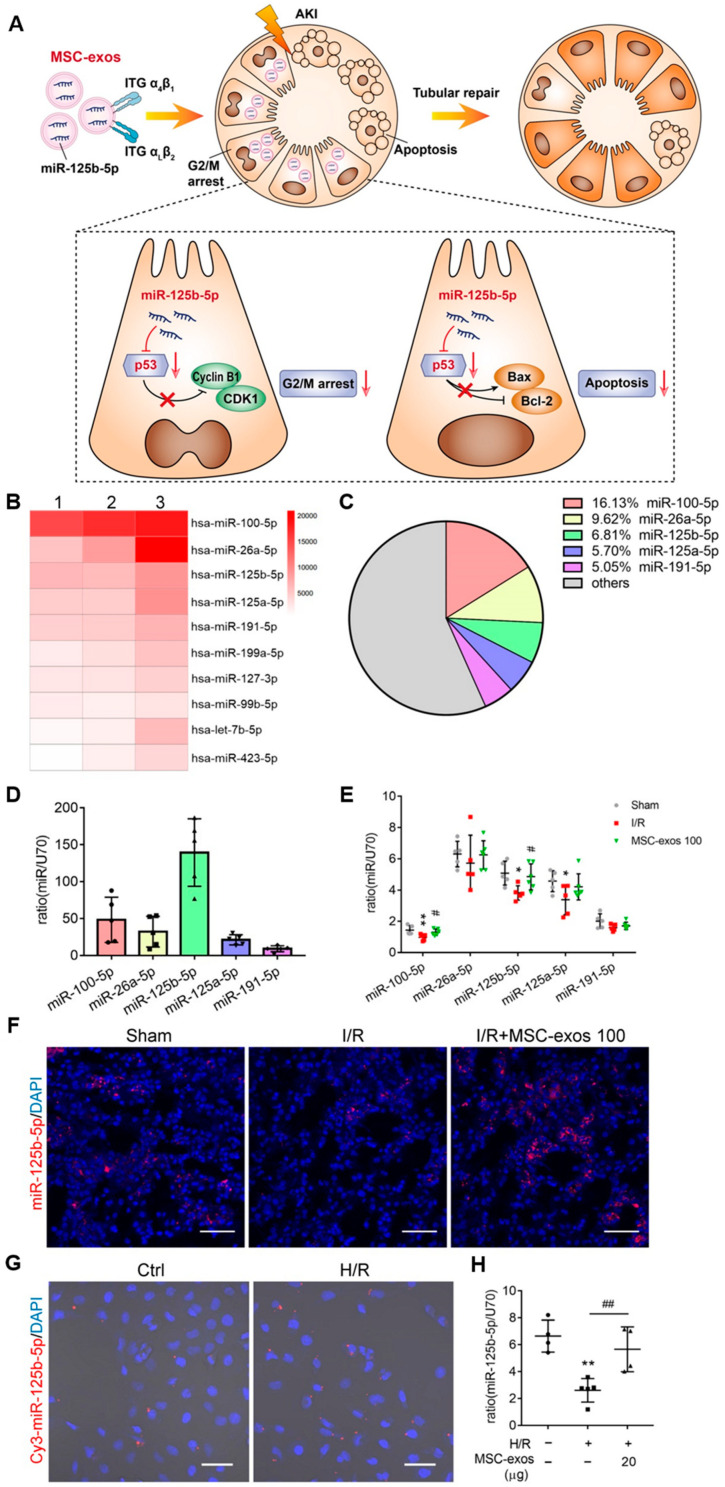
Figure 6.
The miR-125b-5p is enriched in MSC-derived exosomes and delivers to TECs [140]. (A) In ischemic AKI, the injuries of TECs could lead to cell cycle arrest in the G2/M phase and apoptosis. MSC-derived exosomes targeted the injured kidney especially the proximal tubules due to VLA-4 and LFA-1 mediated adhesive interactions. Moreover, miR-125b-5p was enriched in MSC-derived exosomes and exerted the tubular repair effect via suppressing the expression of p53, which not only up-regulated CDK1 and Cyclin B1 to rescue tubular G2/M arrest but modulated Bcl-2 and Bax to inhibit TEC apoptosis. (B) Heat map of the top ten most abundant miRNAs in MSC-exos by miRNA-seq. (C) The relative percentage of miRNAs in total miRNA reads. (D) RT-PCR analysis of the top five most abundant miRNAs in MSC-derived exosomes (n = 5). (E) RT-PCR analysis of the top five miRNAs in MSC-derived-exosome-treated mice renal tissues (n = 5–6). (F) FISH analysis of miR-125b-5p in kidney tissues. Scale bars, 50 µm. (G) Representative images of Cy3-miR-125b-5p mimic-MSC-derived exosomes internalized by HK-2 cells. Scale bars, 50 µm. (H) RT-PCR analysis of miR-125b-5p in HK-2 cells (n = 4–5). Data are presented as mean ± SD, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 vs. sham group or control group, # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01 vs. I/R or H/R group, one-way ANOVA.