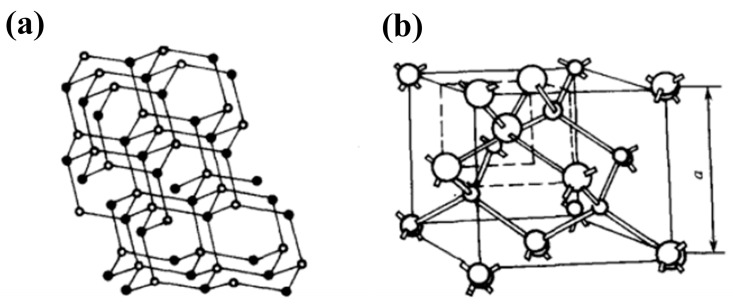
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the diamond (a) crystal structure and (b) crystal cell. Each carbon atom forms a covalent bond with 4 other carbon atoms to form a positive tetrahedron. The strong C-C bonds make diamond hard and have a high melting point. All valence electrons are confined by the covalent bonds, which is why diamond does not conduct electricity [31].