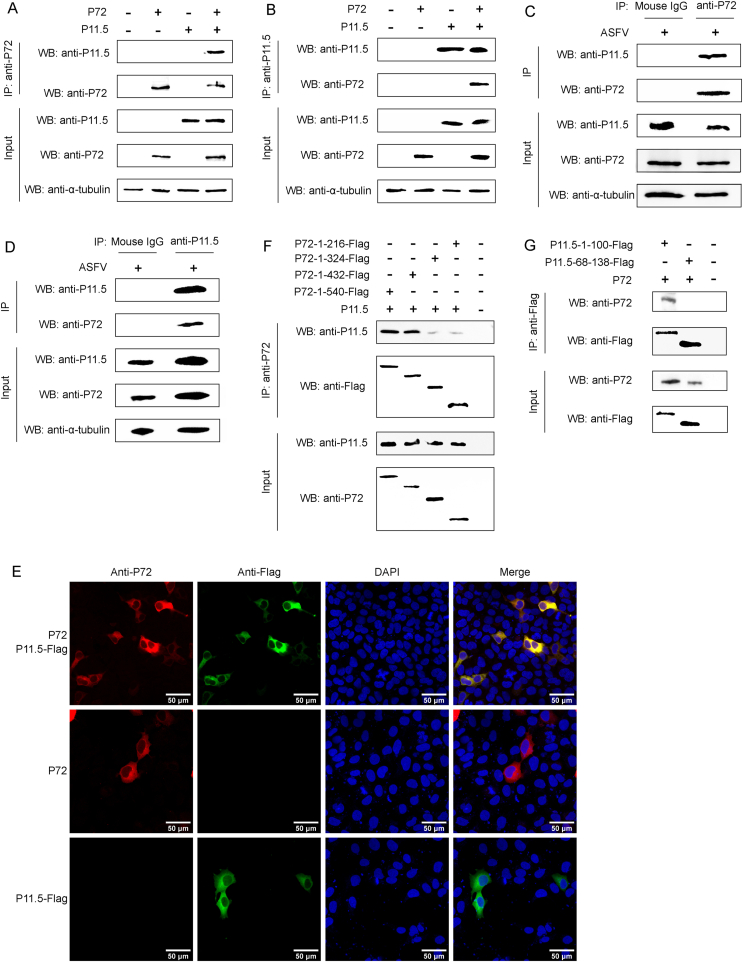
Fig. 2.
Protein p11.5 interacts with p72. A-B HEK293T cells were co-transfected with the pCAGGS-p72 and pCAGGS-p11.5 expression plasmids for 48 h, followed by a CO-IP assay for p11.5 protein and p72 protein using anti-p72 (A) or anti-p11.5 (B) antibody. C-D MA104 cells were infected with ASFVGZ at an MOI of 0.1, and cell extracts were analyzed by Co-IP at 48 h post infection using anti-p72 antibody (C) or anti-p11.5 (D) antibody. (E) MA104 cells were transfected with pCAGGS-p72 and/or pCAGGS-p11.5-Flag expression plasmids for 24 h and then fixed and processed for dual labeling. p11.5 (green) and p72 (red) proteins were visualized by immunostaining with rabbit anti-Flag and mouse anti-p72 antibodies. Cell nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). The areas of colocalization in merged images are shown in yellow. (F) The truncated p72 and full-length p11.5 were co-transfected into HEK293T cells. After 48 h, the cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-p72 and analyzed by WB. (G) The truncated p11.5 and full-length p72 were co-transfected into HEK293T cells. After 48 h, the cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag and analyzed by WB.