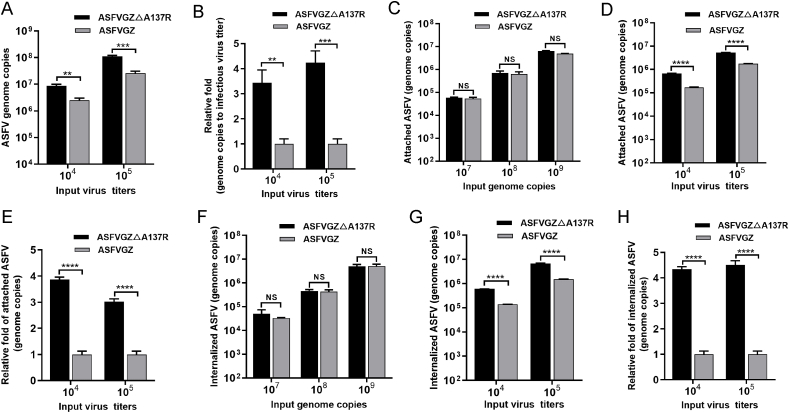
Fig. 6.
The p11.5 protein is not required for ASFV binding to or entry into MA104 cells. A Genome copies of ASFVGZΔA137R or ASFVGZ per 104 and 105 TCID50. B ASFVGZΔA137R or ASFVGZ genome copies-to-infectious virus titer ratios based on samples from panel A. C-D The attachment levels of ASFVGZΔA137R or ASFVGZ were similar. Equal numbers of genome copies (107, 108, and 109) (C) or equal titers (104 and 105) (D) of ASFVGZΔA137R or ASFVGZ were added to MA104 cells at 4 °C and allowed to attach for 2 h. The numbers of genome copies of attached ASFVs were quantified by qPCR. E The fold change in attached ASFVGZΔA137R was nearly 4 times higher than that of ASFVGZ with equal titers (D). F-G The internalization levels of ASFVGZΔA137R or ASFVGZ were similar. Equal numbers of genome copies (107, 108, and 109) (F) or equal titers (104 and 105) (G) of ASFVGZΔA137R or ASFVGZ were added to MA104 cells at 37 °C and allowed to internalize for 2 h. The genome copies of internalized ASFVs were quantified by qPCR. H The fold change in internalized ASFVGZΔA137R was approximately 4 times higher than that of ASFVGZ with equal titers (G). The data shown are from three independent experiments. The significance of differences between groups was determined using Student's t-test (∗∗P < 0.01; ∗∗∗P < 0.001; ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001; NS, not significant).