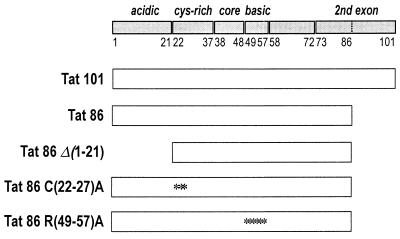
FIG. 1.
Tat proteins and mutants. The Tat protein of HIV-1 and its functional domains are schematically shown. Tat 101 is the full-length, two-exon Tat of most clinical isolates; Tat 86, lacking 15 amino acids at the C terminus, derives from clone HXB2 and is fully active for LTR transcription activation. The mutant proteins include Tat 86 Δ(1-21), which has a truncation in the first 21 amino acids; Tat 86 C(22-27)A, in which cysteines 22, 25, and 27 were mutated to alanines; and Tat 86 R(49-57)A, in which arginines at positions 49, 52, 53, 55, 56, and 57 were mutated to alanines. Asterisks indicate the positions of the mutated amino acids.