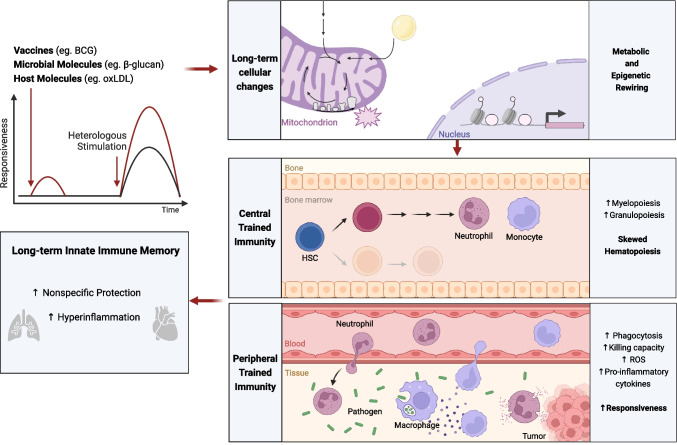
Fig. 1.
Summary of the players involved in innate immune memory. Trained immunity inducers, such as live-attenuated vaccines or microbial and host molecules may trigger metabolic and epigenetic changes. These alterations support a hematopoietic bias towards myelopoiesis and granulopoiesis (i.e. central trained immunity), which leads to the production of trained innate immune cells (eg. neutrophils and monocytes/macrophages). Trained innate immune cells show enhanced effector functions (i.e. peripheral trained immunity), which confers protection against infections or enhances antitumoral activity, or may become maladaptive in the case of hyperinflammatory conditions. Figure created with Biorender.com