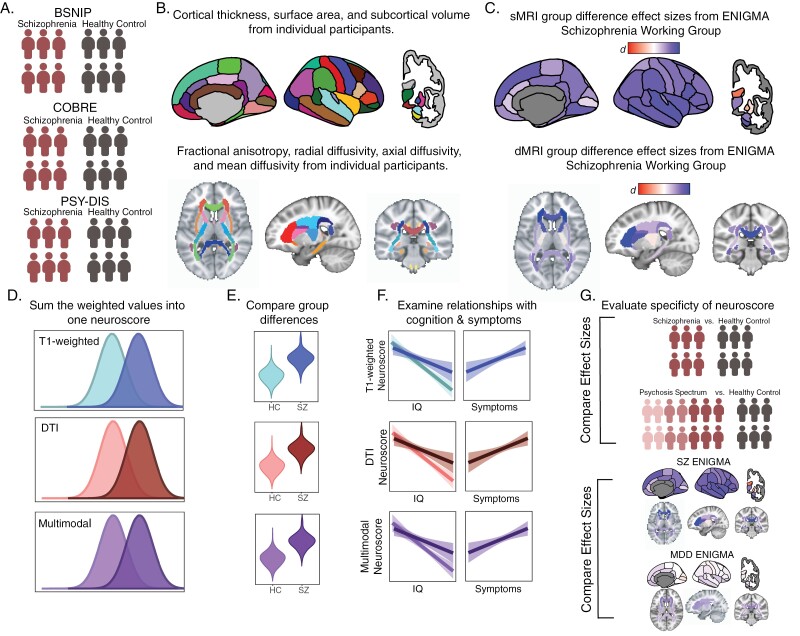
Fig. 1.
Analysis overview. (A) We started with three independent samples containing schizophrenia and healthy controls. (B) MRI measures from T1 and diffusion-weighted images were then calculated for each individual subject and residualized for age and sex. Each MRI measure was then z-scored across the whole sample. (C) Cohen’s d effect sizes were obtained from previously published meta-analyses from the ENIGMA consortium. (D) Individual’s z-scores for each ROI measure were multiplied by the ENIGMA effect size for the corresponding variable and summed across measures to calculate three Neuroscores. (E) We assessed the effectiveness of this score by testing its ability to distinguish cases from controls (F) as well as its relationship to IQ ad positive symptoms. (G) We evaluated the specificity of each Neuroscore by running all analyses (E-F) using a more inclusive psychosis sample and using ENIGMA effect sizes from a study of Major Depressive Disorder. DTI, diffusion tensor imaging; SZ, schizophrenia; MDD, major depressive disorder; sMRI, structural magnetic resonance imaging; dMRI, diffusion magnetic resonance imaging.