Figure 2. MiR-223 deficiency promotes inflammation-associated tumor immunosuppression and PD-1/PD-L1 expression.
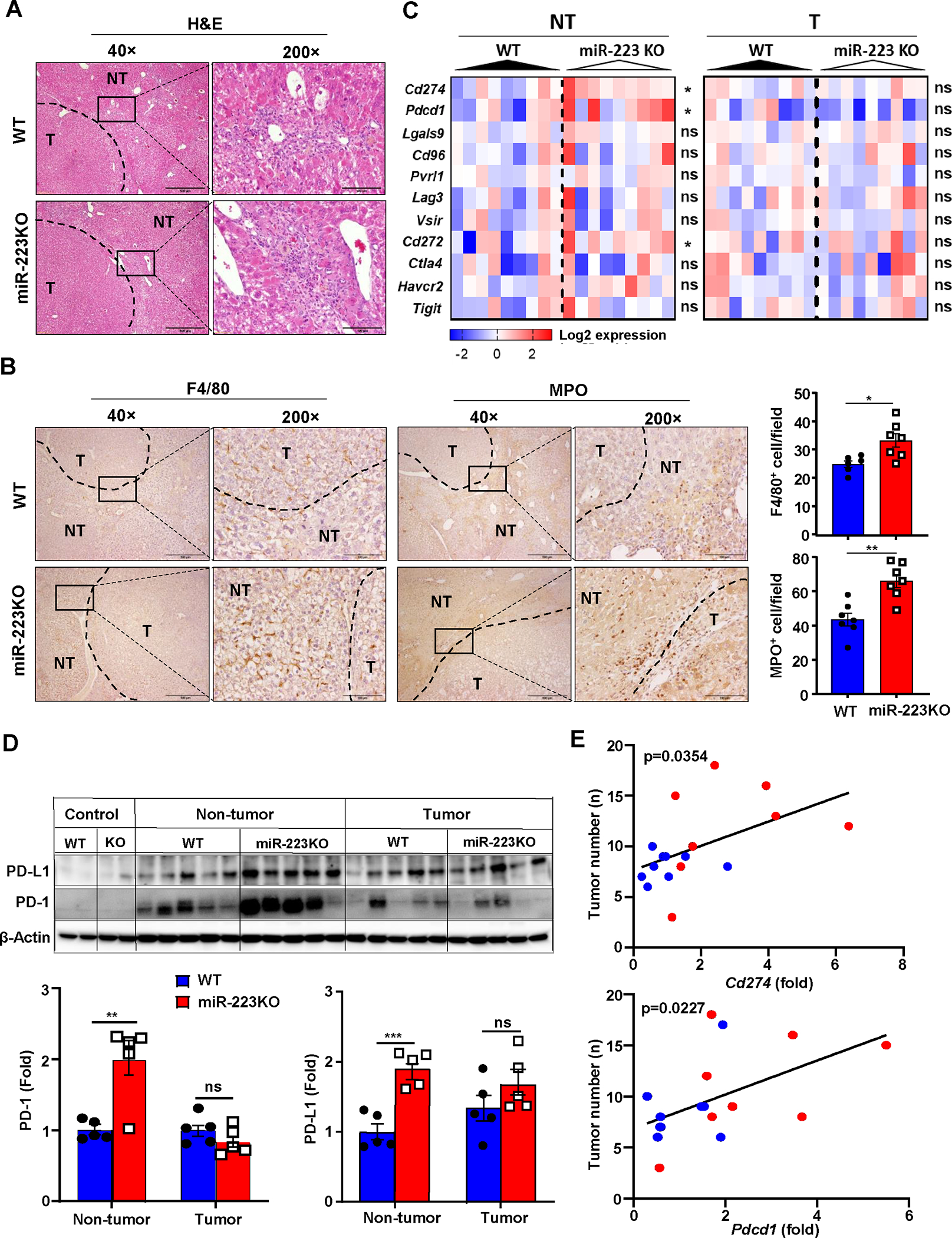
WT and miR-223KO mice were challenged with DEN+CCl4 as described in Figure 1. (A) Representative images of H&E staining in livers from miR-223KO and WT mice are shown. The tumor region was surrounded by dashed line (NT: non-tumor region; T: tumor region). (B) Representative images of F4/80 and MPO staining in non-tumor and tumor regions are shown. F4/80+ and MPO+ cells per field (x200) were quantified. (C) The expression levels of targeted immune checkpoint molecules in non-tumor (NT) and tumor (T) samples were analyzed by RT-qPCR analyses. (D) Western blot analysis PD-1 and PD-L1 proteins in control healthy livers, tumor and adjacent non-tumor samples. (E) Correlation between Pdcd1 or Cd274 expression levels and tumor number in DEN+CCl4-treated WT (n=14, blue dots) and miR-223KO mice (n=9, red dots) was analyzed. Values represent means ± SEM. *P< 0.05, **P< 0.01, ***P< 0.001.
